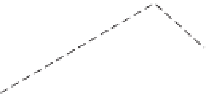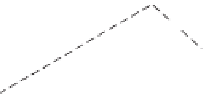Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Box 3.3 Some Basic Features of Soil Clay Minerals and Oxides
Clay minerals have a plate-like crystalline structure for which the flat surface area
is large relative to the edge face area. Figure B3.3.1 shows the basic form of a clay
crystal. There is some substitution of ions of similar size but different positive charge
in the crystal structure, which results in a permanent negative charge in the particle.
The most common substitutions are Al
3+
for Si
4+
,Mg
2+
for Al
3+
, and Fe
2+
for Al
3+
.
Cations in the soil solution are attracted by the permanent negative charge to
the flat clay surfaces—these cations are called exchangeable cations. Depending
on the type of clay mineral, the much smaller edge faces can also attract cations
when the solution pH is above 6 (the edge faces are negatively charged then). At
pH<6,theedgefacesarepositivelychargedandhenceattractanions.
Like the clay mineral edges, Fe and Al oxides show a variable charge that
changes from positive to negative as the solution pH increases—this is referred
to as pH-dependent charge. Up to about pH 8, the oxides are predominantly
positively charged and thus are the main sites for the adsorption of anions such as
H
2
PO
4
−
, Cl
−
, NO
3
−
, SO
4
2−
, and some polyanionic organic compounds. Of these,
H
2
PO
4
−
ions are the most strongly adsorbed because P has a strong affinity for Fe
and Al and bonds chemically to these atoms at the mineral surface.
Highly weathered soils such as Kraznozems (red loams and clay loams rich in
Fe and Al oxides), soils with high organic matter content, and soils derived from
volcanic ash and tephra can be strongly influenced by pH-dependent charges.
Understanding these phenomena is important for the correct management of the
chemical and physical condition of soils.
Planar (cleavage) face
Layer
Crystal
Figure B3.3.1
Diagram of
the structure of a clay crystal
showing crystal layers,
planar (flat) surfaces, and
edge faces. Such a crystal
cannot be seen without a
microscope.
Interlayer space