Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
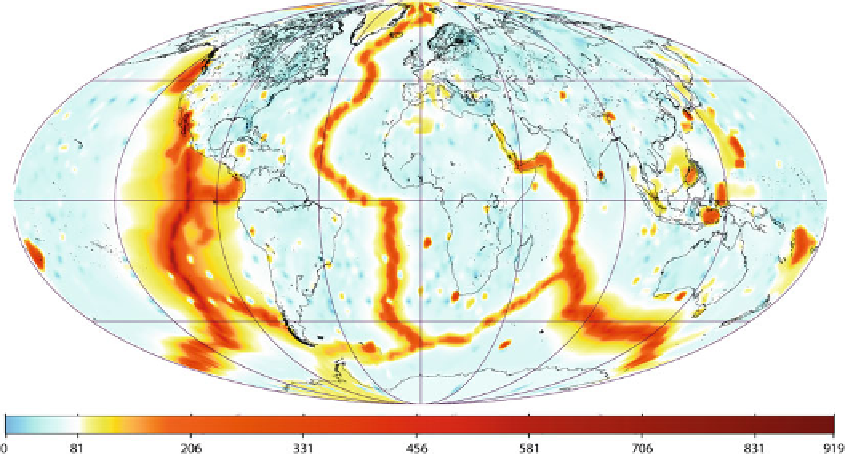
Fig. 12.1
Global map of Earth surface heat flow in mWm
-2
, based on the data of Davies (
2013
)
surface element having normal versor
n
, then the
isotropic Fourier's law reads:
corollary of the complete law of heat conduction
(
12.1
). Combining the two equations gives:
q.n/
D
k
r
T
n
(12.1)
q.n/
D
q
n
(12.3)
where
k
,the
coefficient of thermal conductiv-
ity
, has units Wm
1
K
1
. Therefore, the heat
flux through a surface element
d
S
D
n
dS
is
proportional to the directional derivative of the
temperature field along the direction
n
. Clearly,
changing the orientation of
d
S
will also change
the heat flux through
d
S
. Consequently, Fourier's
law agrees with the quite intuitive concept that the
maximum
heat flow must occur in the direction
of maximum decrease of the temperature field,
which is the direction of -
r
T
. To this purpose, it
is useful to define a vector field
q
D
q
(
r
,
t
)thatis
at any point
r
orthogonal to the isotherm surface
passing through
r
at time
t
. By the properties of
define the vector field of maximum heat flux as
follows:
Measurements of the vertical heat flow
through the Earth's surface are performed
lowering
thermistors
, which are thermally
sensitive semiconductor resistors, down drill
holes. The average heat flux provides essential
information about the quantity of heat that
was generated in the Earth's interior and
the temperature field within the lithosphere.
Figure
12.1
illustrates a recent global compilation
of heat flux data, which is based on
38,000
measurements (Davies
2013
). The average
value of
q
on the continents is relatively
low in N. America, Fennoscandia, and East
Europe (33-40 mWm
-2
), intermediate in Africa
(
52 mWm
-2
), and quite large in Brazil and
Australia (65-68 mWm
-2
). Such a variability
is caused by regional changes in radioactive
heat production. In the oceanic regions, the
average heat flux is greater than
100 mWm
-2
when the lithosphere has an age less than
10 Ma and rapidly decreases in so far as
the age attains 30 Ma (Stein and Stein
1992
).
q
D
k
r
T
(12.2)
Although this equation in many textbooks is
indicated as “Fourier's law”, it represents only a