Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
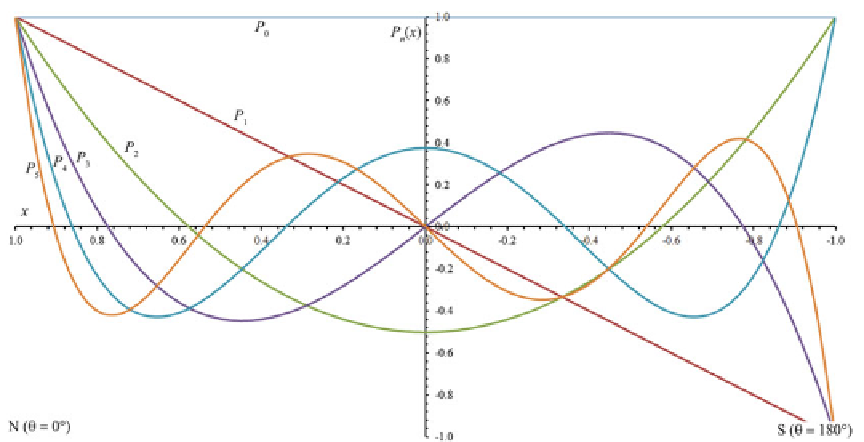
Fig. 4.22
Legendre polynomials for
n
5. Note that the
x
axis scale has been inverted to conform to increasing
colatitudes (from North to South)
parameters
n
and
m
, which are called respectively
degree
and
order
of the solution, must be non
negative integers such that
m
n
. The standard
associate Legendre polynomials are indicated as
P
nm
(
x
). These functions have the form:
P
n
(
x
)). Both the associate and standard Leg-
endre polynomials have specific normalization
properties and satisfy orthogonality conditions.
The normalization of (
4.85
)and(
4.86
) is called
Ferrers normalization
(Winch et al.
2005
). These
functions
satisfy
the
following
orthogonality
T.x/
D
P
nm
.x/
D
.
1/
m
1
x
2
m=2
d
m
conditions:
dx
m
P
n
.x/
(4.85)
Z
C1
2
2n
C
1
.n
C
m/Š
.n
m/Š
•
ns
P
nm
.x/P
sm
.x/dx
D
where the polynomials
P
n
(
x
), which are called
simply
Legendre polynomials
, are defined by the
following Rodrigues' formula:
1
(4.88)
Z
C1
2
2n
C
1
•
ns
dx
n
x
2
d
n
1
n
1
2
n
nŠ
P
n
.x/P
s
.x/dx
D
(4.89)
P
n
.x/
D
(4.86)
1
These polynomials are solutions to the Legen-
dre equation for
m
D
0:
where •
ns
is the Kronecker delta (•
ns
D
1for
n
D
s
and zero otherwise). Setting
n
D
s
in (
4.88
)
gives:
1
x
2
d
2
T
dx
2
2x
dT
dx
C
n.n
C
1/T.x/
D
0
(4.87)
Z
C
1
2
2n
C
1
.n
C
m/Š
.n
m/Š
2
dx
D
j
P
nm
.x/
j
The shape of the first six Legendre poly-
nomials is plotted in Fig.
4.22
. We note that
Legendre functions of even degree are symmetric
about the Equator (
P
n
(
x
)
D
P
n
(
x
)), whereas
they are antisymmetric for
n
odd (i.e.,
P
n
(
x
)
D
1
Therefore, the root-mean-square magnitudes
of
the
Legendre
polynomials
are
subject
to