Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
Ta b l e 2 . 1
Resulted PSNRS (dB) values. NN: Nearest; BL: Bilinear; BC:Bicubic; ND: NEDI;
EO: Edge - oriented; CA-R method
Image
Method
NN
BL
BC
ND
EO
CA-R
Koala (RGB: 256
×
192)
23.70
25.37
25.14
32.45
29.30
30.32
Cameraman (GR:128
×
128)
22.37
23.96
23.70
30.77
25.80
26.54
Lena (RGB:150
×
150)
26.93
28.88
28.77
34.57
30.90
31.57
Box (GR:320
×
240)
28.68
30.19
29.99
32.1
29.13
30.02
Building (RGB:640
×
480)
29.92
31.71
31.73
33.91
30.62
31.58
Teddy (RGB:450
×
376)
10.9374 11.0288
10.96
16.356
13.3263
15.137
Statue (RGB:384
×
288)
24.9064 26.4758 26.2662
29.167
27.3648
28.473
Butterfly (RGB:133
×
100)
18.5155 20.1773 20.1355 25.1367
23.164
24.526
Port (RGB:800
×
600)
24.4053 25.9650 25.8321 29.3648
27.816
28.7912
Garden (RGB:352
×
240)
16.7522 18.0961 19.7002 23.9463 20.1834
21.648
where
MSE
denotes the Mean-Squared-Error and is calculated by:
M
1
i
=
0
−
N
1
i
=
0
[
I
(
i
,
j
)
−
F
(
i
,
j
)]
−
1
2
MSE
=
(2.9)
M
×
N
where
I
is the approximated version
of the image and
M
,
N
are the dimensions of the image, respectively. For color
images, the definition of
PSNR
is the exact same except the
MSE
is the sum over all
squared value differences divided by image size and by three.
All resulted PSNR values for every tested image are provided in Tab. 2.1; while
in Tab. 2.2, the resulted execution time for each method is demonstrated. As it is
depicted in Tab. 2.2, the proposed method produces sufficiently high PSNR values.
Despite their low processing time, the Nearest neighbor method produces zigzag
artifacts over the edge areas while the Bilinear method results in blurred edges. The
Bicubic method also produces blurred edges requiring more processing time. The
highest PSNR values are produced by the NEDI algorithm nevertheless; the required
execution time prohibits its use for real-time applications. The edge-oriented method
produces adequate PSNR values with low processing time however; it is a threshold
dependent method since it is required to determine the edge areas. On the contrary,
the proposed method produces sufficiently high PSNR values preserving the edges
of the initial image. Moreover, exploiting the inherent parallelism of the CA, the
method displays low execution time making appropriate for real time systems.
(
i
,
j
)
corresponds to the original image,
F
(
i
,
j
)


























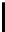


























Search WWH ::

Custom Search