Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
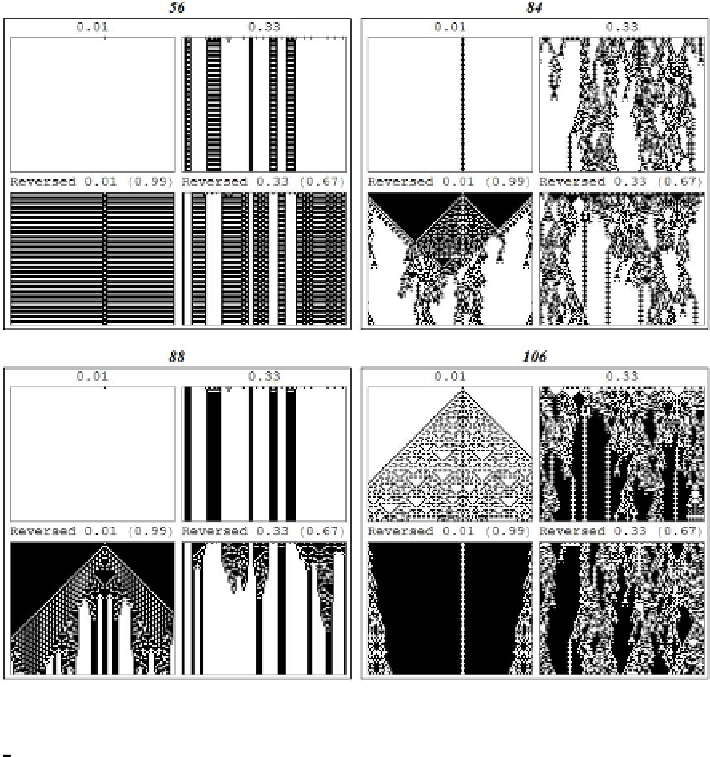
Fig. 11.7
The patterns of T 2-CA rules: 56, 84, 88 and 106. Patterns at the same (coupled)
ICs are shown for each rule: a single 1; below: the corresponding reversed IC with a single 0;
3
3
rate of 1s and the corresponding reversed IC with
0s.
Opacity of the idealized PFSS units is proportional to the angle of rotation: at the
parallel position, that is 0
ⓦ
, the opacity is 0 and at the crossed position, that is 90
ⓦ
,it
is 1. The minimal and maximal opacities occur at
k
180
ⓦ
and
k
180
ⓦ
+
90
ⓦ
,re-
×
×
spectively; where
k
. Since the states of a CA are discrete, it is natural to limit the
rotation angles of polygonal elements to discrete, so called dihedral rotations (DR).
The numbers of DRs for triangle, square, and hexagon are 3, 4 and 6, respectively,
as shown in Fig. 11.8. As Fig. 11.8 indicates, PFSS based on triangular, square, and
hexagonal tessellations have at maximum 3, 2 and 3 distinct opacities, respectively.
However, only the square PFSS renders extreme values from 0 to 1. The triangular
and hexagonal PFSS render three shades of gray: 0.16, 0.5 and 0.83. Square PFSS
can realize any 2C1D CA, the hexagonal and triangular PFSS can realize both two
and three states 1D CA. There are two possible arrangements of cells in the hexag-
onal tessellation. So called “zigzag” tessellation (hexagon-Z) requires one type of
∈
N


Search WWH ::

Custom Search