Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
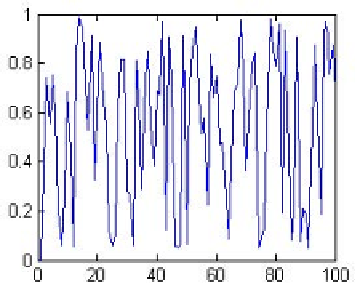
Fig. 7.10
Diffusion Chart for Proposed Secret Key (Average in both scenarios). Row in-
dicates the number of images and column indicates the random number which is between
0 and 1.
Figure 7.10 shows the diffusion chart of our proposed model of generating the
secret key. We only examine XOR local rule for this diffusion evaluation. This fig-
ure exposes high relative distribution index from 0 to 1, indicating well-founded
diffusion for the proposed secret key.
7.4.7
Comparison with Non-CA Works
In Table 7.9, we compared our proposed method with other non-CA algorithms
mentioned in literature review (Section 7.1).
There are two level for digital images encryption; high-level and low-level. In
the high-level encryption the content of the digital image is completely disordered
and the original image is invisible. In low-level encryption, the content of the digital
image is understandable and visible. The proposed algorithm in this chapter gener-
ates visible images (Figure 7.6 and Figure 7.7) and it is not high-level encryption
method in which we will face with really disordered image.
Our proposed CA approach has used the internal information of a digital image
instead of the some logo and external information. Using external logo or other data
may cause to exceed the size of the output images.
7.5
Limitations
The proposed cellular automata's are only one dimensional and it could be consid-
ered as a limitation for our system. The other limitation is using active approach
which is needed the original image for forgery detection. Similarly, we do not
explicitly model noise as an external effect. The main limitation of the proposed
method is sensitivity to post processing.




Search WWH ::

Custom Search