Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
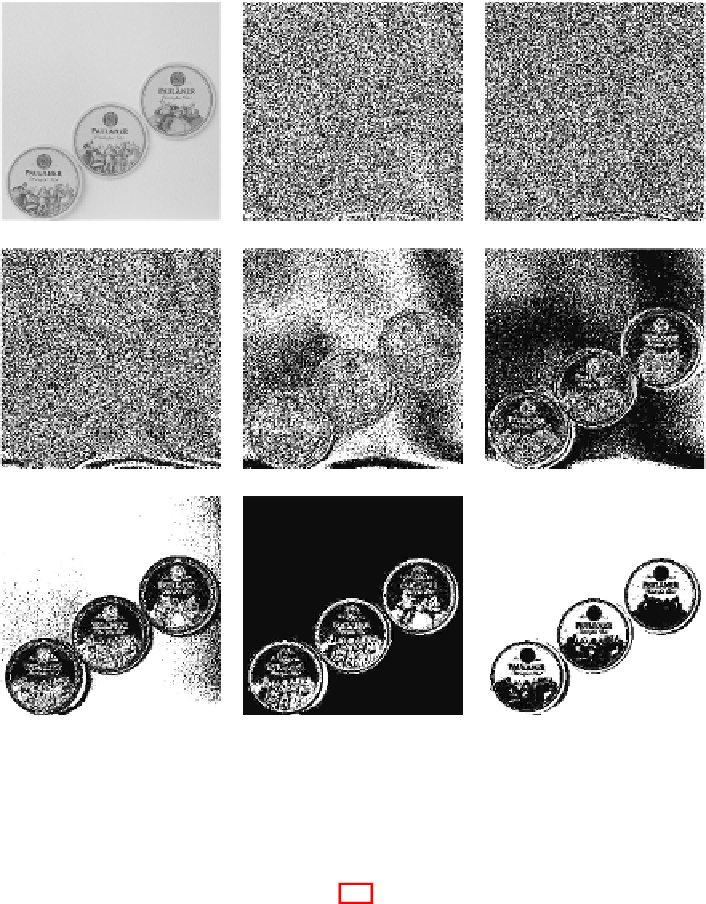
a Grayscale image
b First binary plane
c Second binary plane
d Third binary plane
e Fourth binary plane
f Fifth binary plane
g Sixth binary plane
h Seventh binary plane
i Eight binary plane
Fig. 6.5
Image binary planes
All values of neighbourhood pixels are represented by one bit according to the
value of central pixel, making a binary code that is assigned to the central pixel. An
example of a LBP image is shown in Fig. 6.6. It can be seen that LBP combines good
properties of thresholding and binary planes, because it preserves global shapes and
texture, but it also treats homogeneous region locally leaving enough information
for analysis.
Although the LBP image properly presents texture, it still has the same number of
intensity levels as a greyscale image (256) so it is not appropriate as image represen-
tation for cellular automata. Consequently, representation is defined using LBP but
only for calculating binary values of neighbourhood pixels. Every neighbourhood
is treated separately, and binary values of pixels in that neighbourhood are defined
according to the difference between current pixel and the mean value of all pix-
els in the neighbourhood and current pixel. Those values are then used as a binary
Search WWH ::

Custom Search