Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
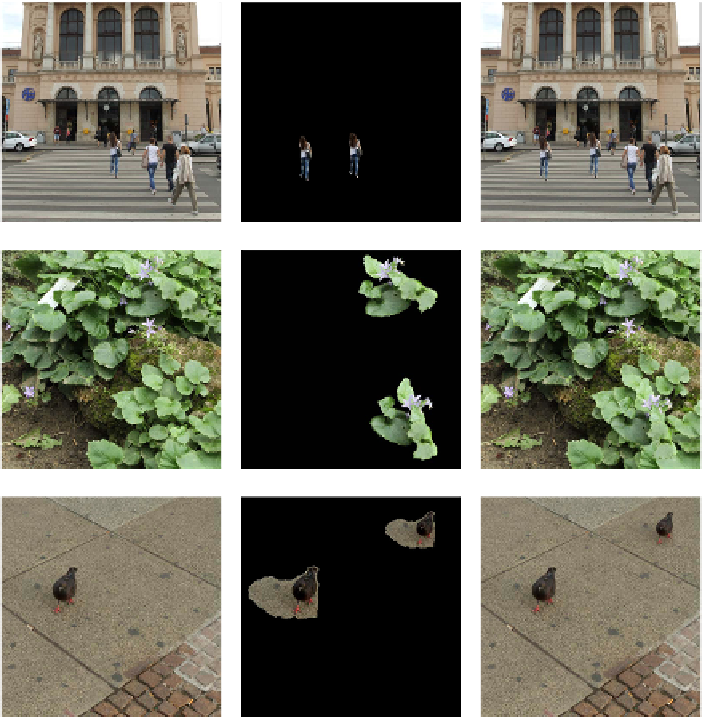
a Plain copy-move forgery (001_F)
b Rotation - rotation angle: 90 degrees (061_F)
c Scaling - scaling factor: 0.7 (098_F)
Fig. 6.1
Examples of CMF (left: original image, middle: regions with copy-move version,
right: forged image). The image identifiers in brackets are provided for comparison with
results in Tab. 6.1.
block-based methods. Keypoint-based methods include scanning of the whole im-
age with the aim of finding points of interest (for example, point with high entropy).
Those points are then analyzed to select only point with the same properties and
detect similar areas in the image. Some popular examples of keypoint-based meth-
ods are SIFT (Scale-invariant feature transform) [1] and SURF (Speeded Up Robust
Features) [21].
Block-based methods involve dividing an image into small overlapping blocks as
a first step of the algorithm. A set of features is then calculated for every defined
block, and those features are used for detection of similar blocks in the image. Dif-
ferent sets of features, such as DCT (Discrete Cosine Transform) [9] / DWT (Dis-
crete Wavelet Transform) [2] coefficients, PCA (Principal Component Analysis)


Search WWH ::

Custom Search