Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
USB on a royalty-free basis, which is perhaps the biggest reason it became more popular
than FireWire in PCs and consumer devices.
1394a Technical Details
The IEEE 1394a standard currently exists with three signaling rates: 100Mbps, 200Mbps,
and400Mbps(12.5MBps,25MBps,and50MBps).Amaximumof63devicescanconnect
to a single IEEE 1394 adapter card by way of daisy-chaining or branching. Unlike USB
devices, 1394devices canbeusedinadaisy-chain withoutusingahub,althoughhubsare
recommended for devices that will be hot-swapped. Cables for IEEE 1394a devices use
NintendoGameBoy-derivedconnectorsandconsistofsixconductors:fourwirestransmit
data and two wires conduct power. Connection with the motherboard is made either by
a dedicated IEEE 1394a interface or by an adapter card.
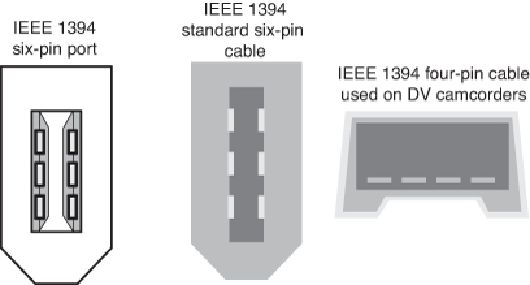
Figure 14.15
shows 1394a port
connectors.
Figure 14.15
IEEE 1394a port connectors.
The1394buswasderivedfromtheFireWirebusoriginallydevelopedbyAppleandTexas
Instruments. The 1394a uses a simple six-wire cable with two differential pairs of clock
and data lines, plus two power lines; the four-wire cable/connector shown in
Figure 14.15
is used with self-powered devices, such as DV camcorders. Just as with USB, 1394 is
fully PnP, including the capability for hot-plugging (insertion and removal of components
without powering down).
Built on a daisy-chained and branched topology, 1394 allows up to 63 nodes, with a chain
of up to 16 devices on each node. If this is not enough, the standard also calls for up to
1,023 bridged buses, which can interconnect more than 64,000 nodes! Additionally, as
with SCSI, 1394 can support devices with various data rates on the same bus. Most 1394
adapters have three nodes, each of which can support 16 devices in a daisy-chain arrange-
ment. Some 1394 adapters also support internal 1394 devices.