Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
This information assumes the data is stored in Mode 1 format, which is used on virtually
all data discs. You can learn more about the Mode 1/Mode 2 formats in the section on the
Yellow Book and XA standards later in this chapter.
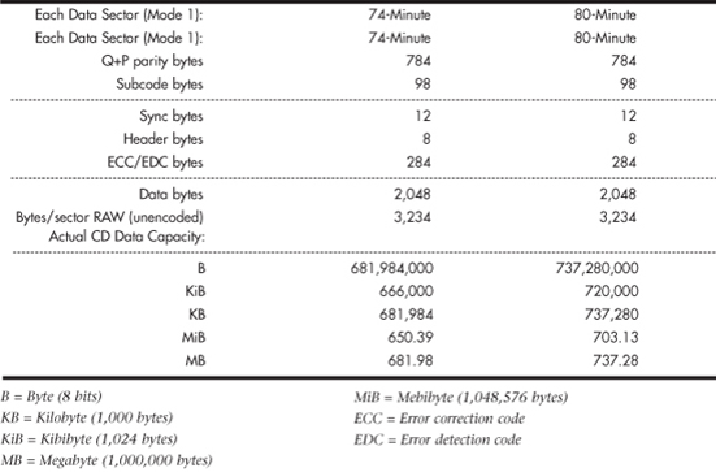
Withdatasectors,youcanseethatoutof3,234actualbytespersector,only2,048areuser
data. Most of the other 1,186 bytes are used for the intensive error-detection and -correc-
tion schemes to ensure error-free performance.
Data Encoding on the Disc
The final part of how data is actually written to the CD is very interesting. After all 98
frames are composed for a sector (whether audio or data), the information is then run
through a final encoding process called
eight to fourteen modulation
(EFM). This scheme
takes each byte (8 bits) and converts it into a 14-bit value for storage. The 14-bit conver-
sion codes are designed so that there are never fewer than two or more than ten adjacent
0 bits. This is a form of Run Length Limited (RLL) encoding called RLL 2,10 (RLL x,y,
where x equals the minimum and y equals the maximum run of 0s). This is designed to
prevent long strings of 0s, which could more easily be misread, as well as to limit the
minimum and maximum frequency of transitions actually placed on the recording media.
Withasfewastwoorasmanyasten0bitsseparating1bitsintherecording,theminimum