Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
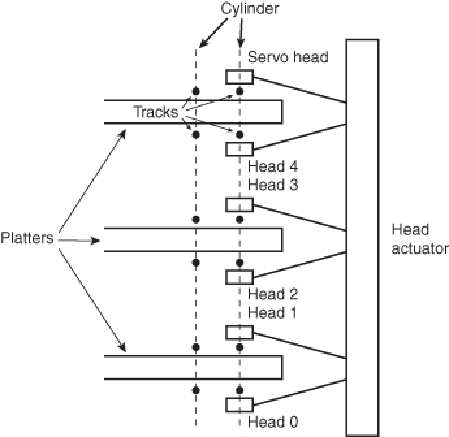
When the drive moves the heads to a specific cylinder, the internal drive electronics use
the signals received by the servo head to determine the position of the read/write heads.
Astheheadsmove,thetrackcountersarereadfromthededicatedservosurface.Whenthe
servo head detects the requested track, the actuator stops. The servo electronics then fine-
tune the position so the heads are precisely above the desired cylinder before any writing
is permitted. Although only one head is used for servo tracking, the other heads are at-
tached to the same rack so that if one head is above the desired cylinder, all the others are
as well.
Onewayoftellingwhetheradriveusesadedicatedservoplatterisifithasanoddnumber
of heads. For example, the Toshiba MK-538FB 1.2GB drive that I used to have in one of
mysystems had8platters, butonly15read/writeheads.Thatdriveusesadedicated servo
positioning system, and the 16th head is the servo head. The advantage of the dedicated
servo concept is that the servo information is continuously available to the drive, making
the head positioning process faster and more precise.
The drawback to a dedicated servo is that dedicating an entire platter surface for servo
information is wasteful. Virtually all drives today use a variation on the embedded servo
technique instead. Some drives combined a dedicated servo with an embedded servo, but
thistypeofhybriddesignisrare.Regardlessofwhethertheservomechanismisdedicated
or embedded, it is far more accurate than the stepper motor mechanisms of the past.