Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
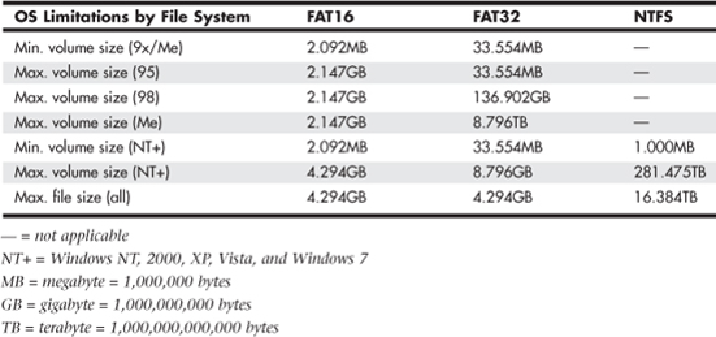
GPT and the 2.2TB Barrier
Although most of the previous barriers in disk capacity have been hardware related, the
2.2TB barrier is more of a software than a hardware problem. Even more specifically, it
is a disk formatting and OS problem, and it's a BIOS problem if you consider boot drives
versus data drives.
This problem stems from the way hard disks have been formatted since DOS 2.0 and
the first PC hard drives appeared in 1983. Back then IBM and Microsoft came up with
a scheme for partitioning drives called the
MBR
(Master Boot Record). The MBR is the
first sector on a disk, and it is internally defined with the ability to control four primary
partitions. Each partition is described by a 16-byte table entry, with 4-byte (32-bit) fields
that define the LBA (Logical Block Address) for both where the partition starts and how
big it is.
The largest number that can be written using 32 binary digits is 2
32
, which is equal to
4,294,967,296. Because each sector is normally limited to 512 bytes, this means that the
maximum amount of a drive that can be recognized is 2.2TB. Combine the MBR limita-
tionwiththefactthatmostPCBIOScanonlybootfromMBR-formatteddrives,andmost
older operating systems only support MBR-formatted drives for both boot drives and data
drives, and you can see that the 2.2TB limitation can be a problem.
Several changes are necessary to break this barrier. The first is to develop a new parti-
tioningschemewithoutthelimitationstheMBRimposes.ThisreplacementiscalledGPT,
which stands for GUID (globally unique identifier) Partition Table. Intel initially deve-
loped the GPT as part of its EFI (Extensible Firmware Interface) specification in 2000;