Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
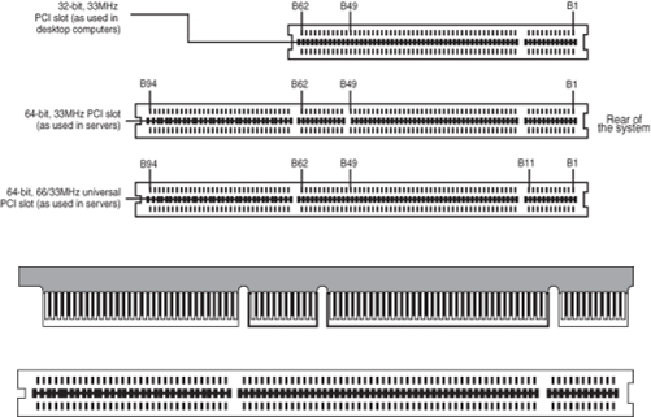
Figure 4.42
A 64-bit universal PCI card (top) compared to the 64-bit universal PCI slot (bottom).
Notice that the universal PCI board specifications effectively combine the 5V and 3.3V
specifications.Forpinsforwhichthevoltageisdifferent,theuniversalspecificationlabels
the pin V I/O. This type of pin represents a special power pin for defining and driving the
PCI signaling rail.
Another important feature of PCI is the fact that it was the model for the Intel PnP spe-
cification. Therefore, PCI cards do not have jumpers and switches and are instead con-
figured through software. True PnP systems are capable of automatically configuring the
adapters, whereas non-PnP systems with ISA slots must configure the adapters through a
program that is usually a part of the system CMOS configuration. Starting in late 1995,
most PC-compatible systems have included a PnP BIOS that allows the automatic PnP
configuration.
PCI Express
During 2001, a group of companies called the Arapahoe Work Group (led primarily by
Intel) developed a draft of a new high-speed bus specification code-named 3GIO (third-
generation I/O). In August 2001, the PCI Special Interest Group (PCI-SIG) agreed to take
over, manage, and promote the 3GIO architecture specification as the future generation of
PCI.InApril2002,the3GIOdraftversion1.0wascompleted,transferredtothePCI-SIG,
andrenamedPCIExpress.FinallyinJuly2002,thePCIExpress1.0specification wasap-
proved. The specification was updated to 1.1 in April 2005, to 2.0 in January 2007 and to
version 3.0 in November 2010.