Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
Power Supply Ratings
A system manufacturer should be able to provide you the technical specifications of the
power supplies it uses in its systems. This type of information can be found in the sys-
tem'stechnicalreferencemanual,aswellasonstickersattacheddirectlytothepowersup-
ply. Power supply manufacturers can also supply this data, which is preferable if you can
identify the manufacturer and contact it directly or via the Web.
The input specifications are listed as voltages, and the output specifications are listed as
amps at several voltage levels. You can convert amperage to wattage by using the follow-
ing simple formula:
watts = volts × amps
For example, if a component is listed as drawing 8 amps of +12V current, that equals 96
watts of power according to the formula.
Bymultiplyingthevoltagebytheamperageavailableateachmainoutputandthenadding
theresults,youcancalculatethetotalcapableoutputwattageofthesupply.Notethatonly
positive voltage outputs are normally used in calculating outputs; the negative outputs,
Standby, Power_Good, and other signals that are not used to power components are usu-
ally exempt.
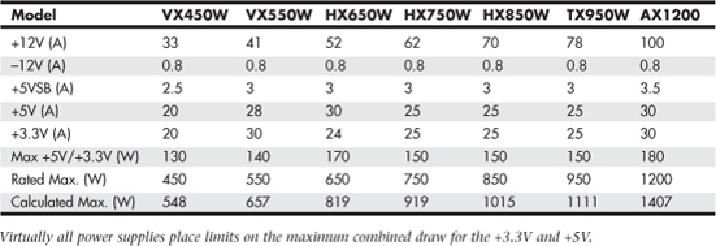
Table 18.25
shows the ratings and calculations for various single +12V rail ATX12V/
EPS12V power supplies from Corsair (
www.corsair.com
)
.
Table 18.25 Typical ATX12V/EPS12V Power Supply Output Ratings
The calculated maximum output assumes the maximum draw from all outputs simultan-
eously and is generally not sustainable. For this reason, the (sustainable) rated maximum
output is normally much less.
Although store-bought PCs often come with lower-rated power supplies of 350 watts or
less, higher output units are often recommended for fully optioned desktops or tower sys-