Hardware Reference
In-Depth Information
costs per month. To determine whether a particular Internet service is using ISDN, you
might need to ask the ISP. For example, AT&T uses the term “Digital Enhancer” for its
ISDN BRI offering in Connecticut, and “Digiline Service” in several plains states.
ISDN doesn't require as high a line quality as DSL, so it can be offered in areas where
DSL can't work without a major upgrade of the telephone system.
Leased Lines
For users with high bandwidth requirements (and deep pockets), dedicated leased lines
provide digital service between two locations at broadband speeds. A
leased line
is a per-
manent 24-hour connection to a particular location that only the telephone company can
change. Businesses use leased lines to connect local area networks (LANs) in remote loc-
ations or to connect to the Internet through a service provider. Leased lines are available
at various speeds, as described in this section.
Toconnectnetworksindistantlocations,networksthatmustsupportalargenumberofIn-
ternet users, or especially organizations that will be hosting their own Internet services, a
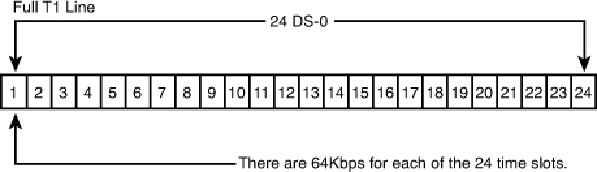
T-1 connection might be a wise investment. A
T-1
is a digital connection running at about
1.5Mbps. A T-1 can be split (or
fractioned
), depending on how it is to be used. It can be
split into 24 individual 64Kbps lines or left as a single high-capacity pipeline. Some ISPs
allow you to lease any portion of a T-1 connection that you want in 64Kbps increments
(or
fractions
).
Figure 16.4
shows how a T-1 line is fractioned.
Figure 16.4
Full T-1 service uses all 24 lines (each one is 64Kbps) as a single pipeline; a fractional T-1 ser-
vice of 256Kbps could use slots 1-4 only, for example.
An individual user of the Internet interacts with a T-1 line only indirectly. No matter how
you're accessing the Internet, your ISP typically will have a connection to one or more
T-1 or T-3 lines, which connect to the backbone of the Internet. This connection to the
backbone is sometimes referred to as a
point of presence
(PoP). When you connect to the
Internet, your ISP shares a small chunk of that pipe with you. Depending on how many
otherusersareaccessing theInternet atyourISPorelsewhere, youmightexperience very
fast to slow throughput, even if your modem connection speed remains constant. It's a
bit like splitting up a pizza into smaller and smaller slices to accommodate more people