Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
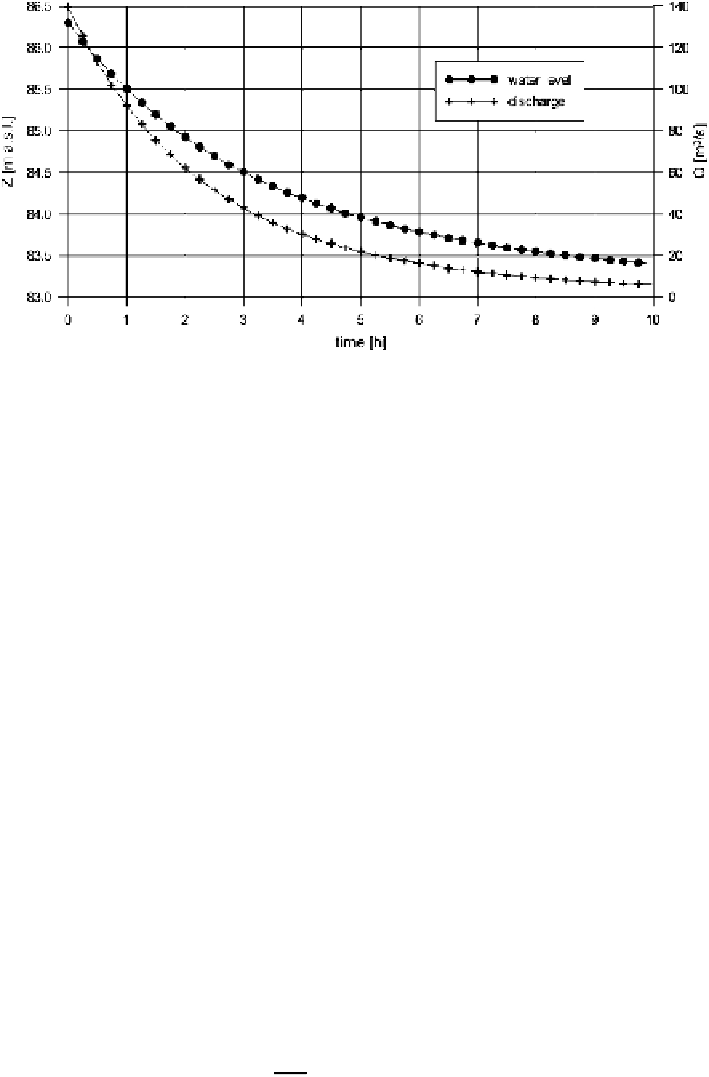
Fig. 3 Outflow hydrograph
3 Hydrodynamics Model and Solution Method
The mathematical model used in the Kolbudy II reservoir case study is a system
of shallow water equations. The model can be presented in conservative form as
(Abbott
1979
):
@
U
t
þ
@
E
x
þ
@
G
y
þ
S
¼
0
(1)
@
@
@
0
@
1
A
;
0
@
1
A
0
h
uh
vh
gh S
ox
S
fx
U
¼
S
¼
(2a,b)
gh S
oy
S
fy
0
@
1
A
;
0
1
uh
u
2
h
vh
uvh
v
2
h
@
A
5
gh
2
E
¼
þ
0
:
G
¼
(2c,d)
5
gh
2
uvh
þ
0
:
In the system of (
1
) and (2):
t
¼
time; (
x, y
)
¼
horizontal coordinates; (
u, v
)
¼
depth-averaged velocities in
x
and
y
directions;
h
¼
local depth;
S
ox
,
S
oy
¼
bed
slopes in
x
and
y
directions;
S
fx
,
S
fy
¼
bottom friction terms in
x
and
y
directions
defined by Manning formula;
g
¼
gravity. Equation
1
can be presented in another
vector form as (LeVeque
2002
):
@
U
t
þr
F
þ
S
¼
0
(3)
@
(
n
x
,
n
y
)
T
is an unit vector.
where vector F is defined as Fn
¼
E
n
x
+ G
n
y
and n
¼