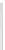Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
4.3 Experimental Facilities and Instrumentation
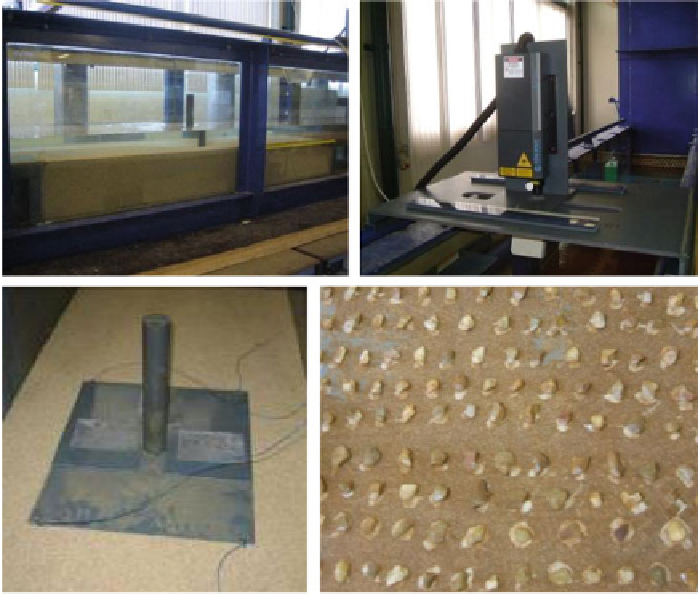
The experiments were conducted in a 8.0 m long and 0.70 m wide rectangular
flume. The flow discharge was controlled by a flow meter installed in the pumping
circuit, and the flow depth was controlled by the adjustment of the downstream
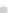
gate. A horizontal mobile bed reach 2.00 m long was placed 4.55 m downstream of
the flume inlet (Fig.
32a
). In the upstream reach of the mobile bed, uniform quartz
sand was glued on the flow bed, in order to increase its roughness. The bed material,
used both on mobile and fixed bed, is characterized by a median diameter
d
50
of
0.837 mm and geometric standard deviation s
D
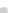
of 1.48. The PIV laser source
was attached on a mobile carriage, settled on the longitudinal rails of the channel
(Fig.
32b
). The cylinder (PVC), with 0.048 m diameter, was placed in the sym-
metry axis of the channel (Fig.
32c
). To investigate the effect of the roughness
in the development of the turbulent boundary layer, velocity measurements on
the approach flow were accomplished before and after the placement of granular
material with 25 mm of characteristic diameter, in the upstream region of the flow
a
b
laser head
optics
ruler
mobile bedreach
mobile carriage
c
d
c
ilindrical
pier
protection plate
granular material
Fig. 32 Experimental details (a) mobile bed reach, (b) laser source, (c) cylinder, and (d) disposal
of granular material at the upstream reach of the channel