Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
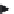
V
= j
wL
I
f
= 90°
I
Figure 2.8
Phasor diagram for inductance
I
f
= -90°
V
= -j(1 /
wC
)
I
= (1 /j
wC
)
I
Figure 2.9
Phasor diagram for capacitance
We may obtain the power and reactive power in the inductance from (2.14):
P
¼
VI
cos
f ¼
0
Q
¼
VI
sin
f ¼
VI
¼
XI
2
An inductive load absorbs positive reactive power.
Capacitance (C)
Capacitive current may be related to the voltage drop across it by consideration of
rate of change of charge:
q
¼
Cv
d
q
d
t
¼
C
d
v
i
¼
d
t
1
w
C
I
m
cos
ðw
t
p=
2
Þ
In this case the voltage phasor lags the current phasor by 90
(
p
/2 rad). This corre-
sponds to a phase shift of
j. The corresponding phasor diagram is shown in Figure 2.9.
The complex impedance of the capacitance is
Z
¼
1/j
w
C
and the capacitive
reactance or impedance magnitude is given by
X
¼
1/
w
C
.
The power and reactive power taken by the capacitor are given by (2.14):
∴
v
¼
P
¼
VI
cos
f ¼
0
Q
¼
VI
sin
f ¼
VI


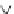











Search WWH ::

Custom Search