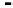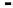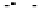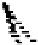Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
inspection of Eq. (1-29), it can be seen that the units for r are time
1
; for
example, hours
1
, min
1
,ordays
1
. In Figure 1-24, we plot the drug
concentration C(t) versus time with C(0)
¼
4
m
g/ml and for three
0.1 hours
1
.
different values of r: r
¼
0.3, r
¼
0.2, and r
¼
The elimination parameter r is closely related to the drug's half-life,
,
defined as the time necessary to reduce the concentration of the drug in
the blood by 50%. In mathematical terms, the half-life
t
is the time
t
elapsed since the initial moment t
¼
0 for which C(
)
¼
0.5C(0). Using
t
Eq. (1-30) gives us C(0)e
r
t
¼
0.5C(0), or e
r
t
¼
ln(0.5),
leading to the following connection between the elimination rate
0.5. Thus
r
t
¼
ln
ð
2
Þ
constant r and the drug's half-life:
t
¼
:
r
E
XERCISE
1-16
0.2 hours
1
,
From the graph in Figure 1-24, corresponding to r
¼
estimate the drug's half-life; then compute
from the equation above
t
and compare the two values.
E
XERCISE
1-17
The half-life of acetaminophen is 2.5 hours. If a single dose is
administered at 12:00 noon, how long will it take for the
4.5
4
3.5
3
2.5
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
Time
FIGURE 1-24.
Serum drug concentration for different values of r. From top to bottom, the graph corresponds to
r ¼ 0.1, r ¼ 0.2, and r ¼ 0.3 hours
1
, respectively. Larger values of r signify faster elimination of the
drug from the bloodstream.