Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
If the cDNAs are to be made by cloning, recombinant plasmids bearing
the cDNAs are introduced into bacteria, which will then make many
copies of the cDNAs. If the cDNAs are to be amplified via PCR, the
replicative power of the Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase is used to
make the copies. If the microarray is to contain oligonucleotides, a DNA
synthesizer is programmed to produce DNAs with the desired
sequences.
Once the DNAs are produced, they may be spotted onto the solid
support by inkjet-style printer heads or by pins dipped into the DNA
and then touched to the surface of the support. Robots move the inkjets
or pins, so that the placement of features is precise and reproducible.
The use of robots allows high-density placement of tiny features. Each of
the thousands of spots on a single slide may represent a different gene.
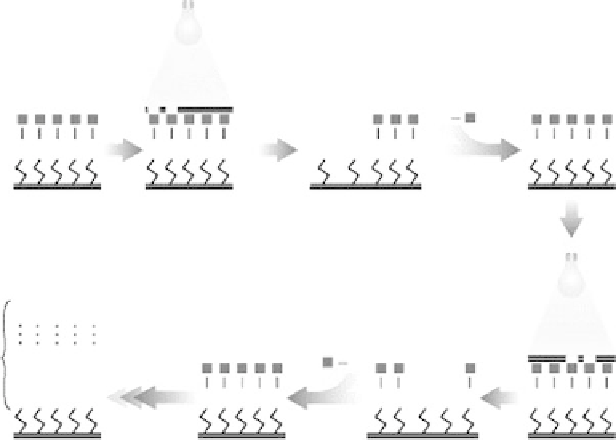
In photolithography, on the other hand, the oligonucleotides are
synthesized in place in a process which is akin to that used to produce
integrated circuits. Light is used to activate one step in the process,
and masks are used to block the light for those portions of the chip that
are not to participate in the reaction. The process employed by
Affymetrix, Inc. to produce its widely used GeneChip
W
is shown in
Figure 12-5. The first step in the manufacturing process requires that
a quartz wafer be covered with a light-sensitive protecting group. This
group binds to all available sites on the wafer and prevents nucleotides
Light
(deprotection)
Mask
T
OO
OOO
OOOOO
OH O O O
T
T
O O O
OH
Water
G
A
T
CG
25-mer
C
A
TT
A
C
A
TT
GC
CC
TG
G
TT
CC
O
TT
OHOHO
TTOOO
Repeat
GeneChip
®
Microarray
FIGURE 12-5.
Affymetrix, Inc. uses a unique combination of photolithography and combinatorial chemistry to
manufacture GeneChip
W
Arrays. (Image courtesy of Affymetrix, Inc.)