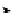Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
100
Hypoglycemia
Target Range
Hyperglycemia
80
60
Low BG Risk
High BG Risk
40
Clinical and
Numerical
Center
20
0
−
3
−
2.5
−
2
−
1.5
−
1
−
0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
Transformed BG Scale
f
(
BG
)
FIGURE 5-8.
The BG risk function. Note that the clinical and numerical centers are now the same. (From
Kovatchev, B. P., Straume, M., Cox, D. J., & Farhi, L. S. [2001]. Risk analysis of blood glucose data:
A quantitative approach to optimizing the control of insulin dependent diabetes. Journal of Theoretical
Medicine, 3, 1-10. Used by permission of Taylor & Francis, Ltd. [
http://www.informaworld.com]).
scale. The equation of the BG risk function in Figure 5-8 is:
r(BG)
10[ f (BG)]
2
.
¼
Now we can better understand the calibration condition imposed
on the transformation f (BG) earlier. Because f (BG) ranges from
1
p
, the risk function r (BG) ranges from 0 to 100. Its minimum
value of 0 is achieved at f (BG)
1
p
to
¼
6.25 mmol/L. The maximum is reached at the extreme ends of the BG
scale, f
¼
0 or, in the original scale, BG
Þ¼
1
p
, i.e., BG
ð
BG
¼
1.1 mmol/L in the original scale (extreme
Þ¼
1
p
, i.e., BG
hypoglycemia) and f
33.3 mmol/L in the
original scale (extreme hyperglycemia). Thus, r (BG) can be interpreted
as a measure of the risk associated with a certain BG level. The left
branch of this parabola identifies the risk of hypoglycemia, whereas the
right identifies the risk of hyperglycemia. Notice, again, that
because in this scale the hypo- and hyperglycemic ranges of the BG
scale are symmetric about 0, the symmetric risk function in
Figure 5-8 would be equally sensitive to hypoglycemic and to
hyperglycemic readings.
ð
BG
¼
For comparison, Figure 5-9 presents r (BG) in the original BG scale. As
you may have expected, the risk function in this scale increases much
more rapidly in the hypoglycemic range and thus is not equally sensitive
to hypoglycemic and to hyperglycemic readings.
E
XERCISE
5-2
Compute the risk function for the following BG readings: 1.8 mmol/L,
3.9 mmol/L, 6.25 mmol/L, and 24.6 mmol/L.