Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Trees
Trees
Upland
Low-growing
vegetation
Stream base
flow or
waterbody
Riparian-associated
groundwater
Riparian zone
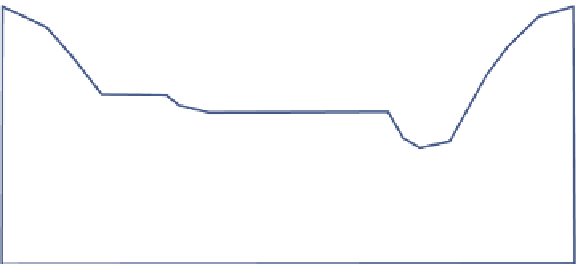
FIGURE 2.22
Schematic of a generic riparian zone showing zone of inluence. (Based on NRCS, Riparian
areas environmental uniqueness, functions, and values, RCA Issue Brief #11, United States Department of
Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service, Washington, DC, 1996.)
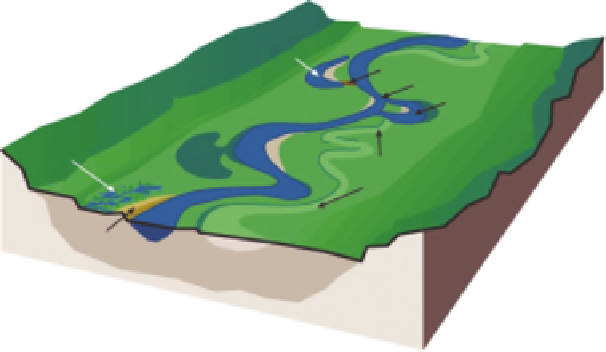
Oxbow
lake
Clay plug
Chute
Oxbow
Backswamp
Splay
Meander
scrolls
Natural
levee
FIGURE 2.23
Landforms and deposits. (From FISRWG,
Stream Corridor Restoration: Principles,
Processes, and Practices
, Federal Interagency Stream Restoration Working Group, 1998.)
•
Oxbow lake: a body of water created after clay plugs the oxbow from the main channel.
•
Natural levees: the formations that build up along the bank of streams that lood. As
sediment-laden water spills over the bank, the sudden loss of depth and velocity causes
coarser-sized sediment to drop out of suspension and collect along the edge of the stream.
•
Splays: delta-shaped deposits of coarser sediments that occur when a natural levee is
breached. Natural levees and splays can prevent loodwaters from returning to the channel
when loodwaters recede.
•
Backswamps
: a term used to describe loodplain wetlands formed by natural levees.
2.2.2.3 Upland Areas
The upland areas are those above the existing loodplain and are connected to the loodplain by an
upland fringe. The fringes have no typically deining shapes or features. One example of a fringe
that has resulted from changes in the loodplains is terraces (FISRWG 1998).









































Search WWH ::

Custom Search