Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
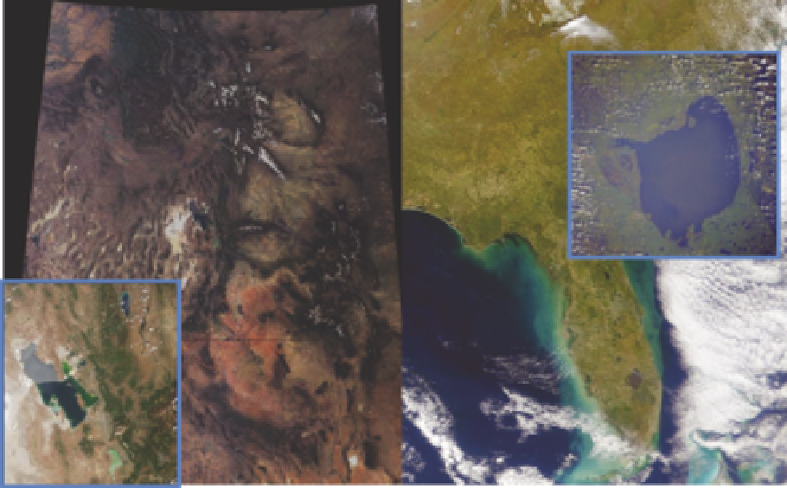
FIGURE 9.8
Utah and the Great Salt Lake (
left
) and Florida and Lake Okeechobee (
right
) as seen from
space. (Courtesy of NASA.)
limited productivity. Caldera basins, such as Crater Lake in Oregon, are formed by the collapse of
a volcanic cone (Figure 9.9). Crater Lake is the seventh deepest lake in the world, with a depth of
608 m (Wetzel 2001). An example of a lake formed behind volcanic debris lows is Spirit Lake in
Washington, which was formed behind debris lows from Mount St. Helens.
9.3.1.3 Glacial Basins
These basins include moraines, formed by the debris from glaciers; cirques, formed in the eroded
head of a glacial valley; and tarns, formed by freezing and thawing. The Laurentian Great Lakes are
FIGURE 9.9
Crater Lake. (Courtesy of USGS Crater Lake Data Clearinghouse.)

Search WWH ::

Custom Search