Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Set general goals
Habitat
assessment
Set specific objectives and set design criteria
Obtain approval from project stakeholders
Prepare sediment studies plan
Ye s
Determine values for design discharge
and bed material gradation
No
Can overall goals be
met by alternate
design?
Conduct a stability assessment
No
Does project involve channel reconstruction?
Ye s
No
Will channel boundary be mobile at design discharge?
�reshold approaches
to obtain channel width,
depth, and slope
Active bed approaches
to obtain channel width,
depth, and slope
Determine planform geometry and lay out channel right-of-way
Add geometric detail (physical variability) and habitat features
Check stability of restored channel under
projected postconstruction conditions
No
Is stability satisfactory?
Implementation/construction
Monitoring
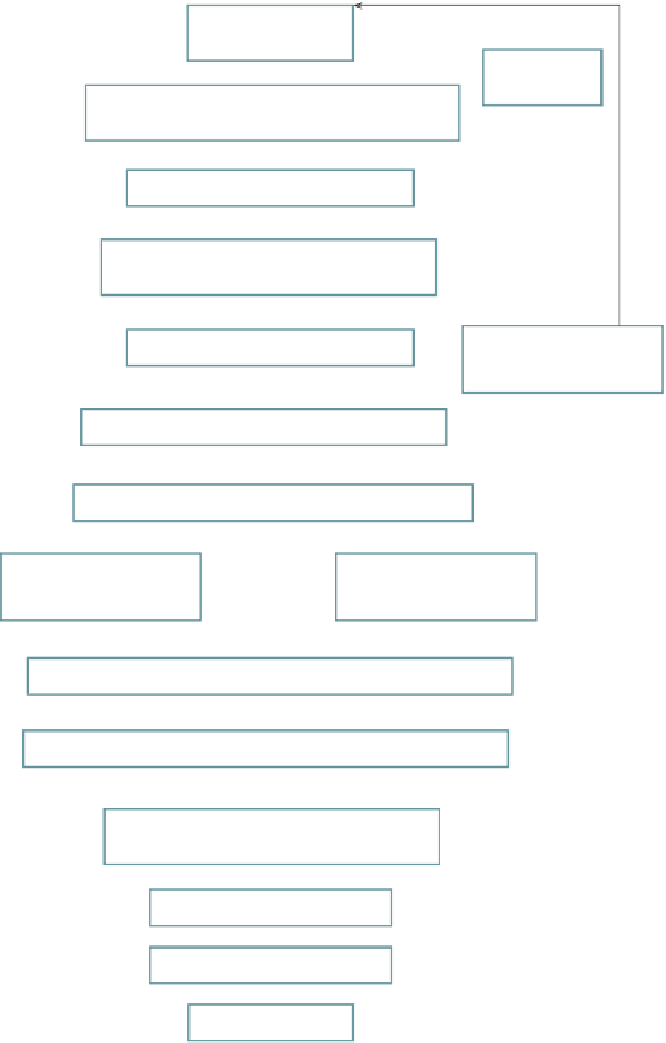
FIGURE 8.6
Flow chart for hydraulic engineer's aspects of restoration projects. (Redrawn from Shields,
F.D., Cooper Jr., C.M., Knight, S.S., and Moore, M.T.,
Ecological Engineering
, 20, 441-454, 2003a; Shields
Jr., F.D., Copeland, R., Klingeman, P.C., Doyle, M.W., and Simon, A.,
Sedimentation Engineering
, American
Society of Civil Engineers, Reston, VA, 2008. With permission from the American Society of Civil Engineers.)
8.4.1 a
GrIcuLturaL
b
eSt
M
anaGeMent
p
ractIceS
Best management practices (BMPs) are generally understood as practices that are intended
to reduce the pollutant content of nonpoint source discharges, such as pathogens or indica-
tor species (e.g., coliform bacteria), pesticides, organic materials, sediments, and nutrients.





































Search WWH ::

Custom Search