Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
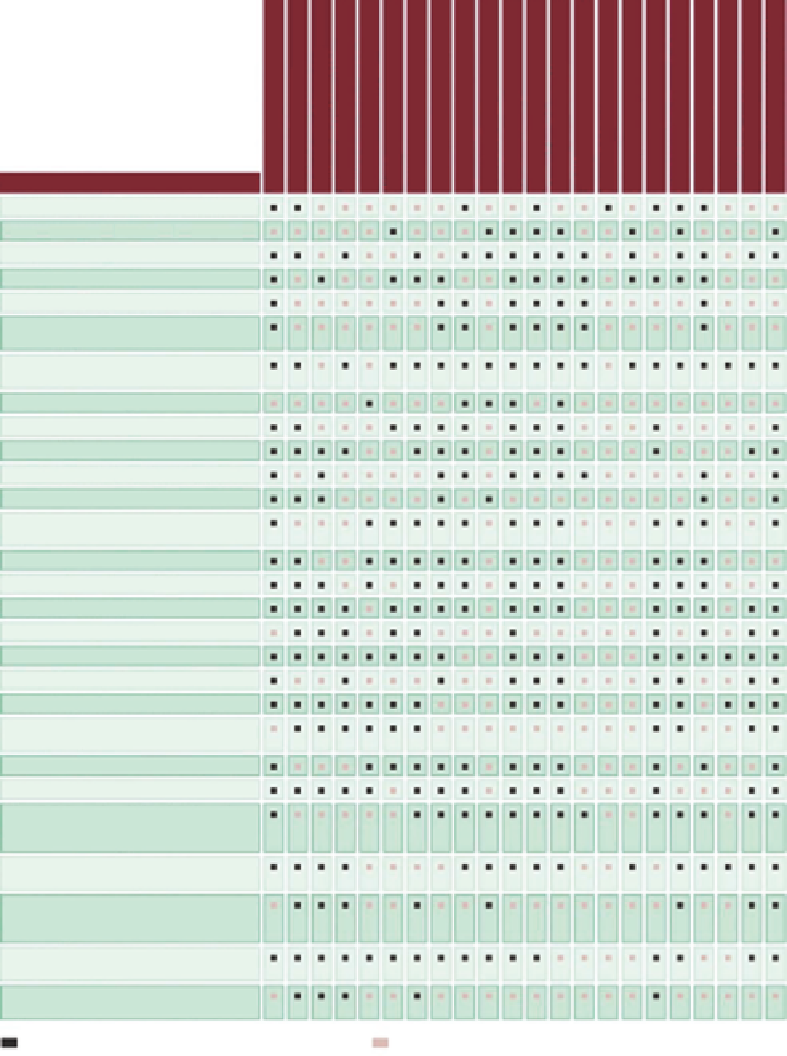
Potential effects
Homogenization of landscape elements
Point source pollution
Nonpoint source pollution
Dense compacted soil
Increased upland surface runoff
Increased sheetflow w/surface erosion
rill and gully flow
Increased levels of fine sediment and
contaminants in stream corridor
Increased soil salinity
Increased peak flood elevation
Increased flood energy
Decreased infiltration of surface runoff
Decreased interflow and subsurface flow
Reduced ground water recharge and
aquifer volumes
Increased depth to ground water
Decreased ground water inflow to stream
Increased flow velocities
Reduced stream meander
Increased or decreased stream stability
Increased stream migration
Channel widening and downcutting
Increased stream gradient and reduced
energy dissipation
Increased or decreased flow frequency
Reduced flow duration
Decreased capacity of floodplain and
upland to accumulate, store and filter
materials and energy
Increased levels of sediment and
contaminants reaching stream
Decreased capacity of stream to
accumulate and store or filter materials
and energy
Reduced stream capacity to assimilate
nutrients/pesticides
Confined stream channel w/little
opportunity for habitat development
(a)
Activity has potential for direct impact.
Activity has potential for indirect impact.
FIGURE 8.5
(a,b) Potential effects of major land use activities. (From FISRWG,
Stream Corridor
Restoration: Principles, Processes, and Practices
, Federal Interagency Stream Restoration Working Group,
1998.)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search