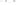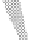Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
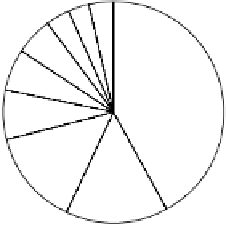
West Europe 3.1
3.6 Others
Caspian Basin 3.5
Asia and Pacific 5.
5
South and
Central America
6.1
42
Middle East
North and
West Africa
7.2
15
North
America
Russia 14
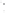
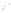
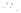
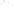
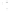
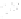
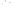
Figure 2.14
World's oil reserves, percent. (Data from U.S. Geological Survey, 1997.
Ranking of the World's
Oil and Gas Provinces by Known Petroleum Volumes
. Report 97-463.)
2.7.3
Unconventional Petroleum Resources
In addition to conventional oil reserves, vast amounts of hydrocarbon fluids are distributed in various
geological formations, such as oil shales and tar sands. Oil shale deposits are known to exist in
the United States in the Colorado Basin (Colorado, Utah, and Wyoming) and in the Appalachian
Basin (Pennsylvania, Virginia, and West Virginia). Tar sands are found in the Canadian Province
of Alberta, as well as in Venezuela and Colombia. In the United States alone, it is estimated that
deposits of oil shale contain perhaps close to 2000 Q of petroleum. With an estimated recovery
factor of 60%, the U.S. oil shales may contain up to 1200 Q. This is about 10 times as much as
the proven oil reserves in the United States. However, the exploitation of these unconventional
petroleum resources may require greater financial and technological investments than those for
the discovery and extraction of oil reserves. Furthermore, the extraction of petroleum from oil
shale may impact the environment to a greater degree than that of pumping oil from on- or off-
shore wells. On the average, oil shales contain between 60 and 120 liters of petroleum per ton of
shale rock. The rock must be excavated and heated in retorts to drive out the liquid petroleum. Thus,
a significant fraction of the derived petroleum must be burnt in order to heat the rock for further
extraction of petroleum. The process will require complex and expensive control technology for
the prevention of air emissions and liquid effluents. Also, the spent rock must be disposed of in an
environmentally safe and aesthetic manner. The environmental controls alone will add greatly to
the cost of extracting petroleum from the unconventional resources. After the OPEC oil embargoes
in the 1970s, a consortium of oil companies started to produce pilot scale quantities of petroleum
products from oil shale deposits in Colorado. However, after the prices of crude oil fell from a
high of $35 per barrel in 1981 to the teens in the late 1980s, all oil shale activities in the United
States ceased.
2.7.4
Natural Gas Reserves
The combustible part of natural gas (NG) consists mainly of methane (CH
4
) with some admixture
of heavier hydrocarbons (ethane, propane, and butane). However, frequently noncombustible gases
are found mixed with NG, namely, N
2
and CO
2
. For example, the recently discovered gas fields
off the coast of the Indonesian archipelago contain up to 70% by volume CO
2
. On the average,
NG contains 74.4% by weight of carbon, 24.8% hydrogen, 0.6% nitrogen, and 0.2% oxygen.