Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
0
1
2
3
V/ V
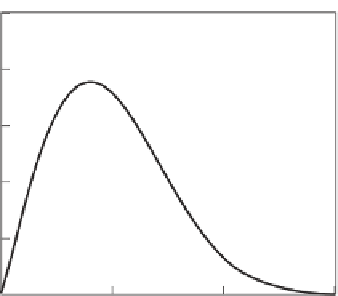
Figure 7.19
A probability distribution
p
{
V
}
of wind speed at a site for which the average speed is
V
shows
low values at low and high speeds and a maximum near the average speed.
a suitable wind turbine design. A commonly used form of the probability distribution function of
wind speeds is
exp
2
V
V
}=
2
V
V
2
−
4
p
{
V
(7.15)
where
p
is the probability of a wind speed
V
, per unit of wind speed, at a site where
V
is the time-averaged wind speed.
21
In Figure 7.19, it can be seen that a very low or high wi
nd
speed, compared to the average, is very unlikely, and that the mo
st p
robable wind speed is 0
{
V
}
8
V
.
In addition, the average value of the cube of
th
e wind s
pe
ed,
V
3
,
to
which the average wind
power is proportional, can
be
calculated to be
V
3
.
V
3
91
V
3
. Thus the average value
=
(
6
/π)
=
1
.
of
th
e wind energy flux
ρ
V
3
/
2 is considerably more than its value at the average wind speed,
3
ρ(
2.
At any site, wind speed and energy flux increase gradually with distance
z
above ground level.
While it is theoretically advantageous to place a wind turbine on a high tower so as to take advantage
of the higher energy flux available there, the greater cost of a higher tower may not be offset by
a less costly turbine. Generally, tower height is proportional to turbine diameter, the turbine axis
being about one to two diameters above ground.
Wind turbines need to be protected from damage by storm or hurricane level winds and, in
northern climates, from icing conditions in winter months.
Wind turbines are customarily installed at adjacent sites called “wind farms,” an example of
which is shown in Figure 7.20. Currently, wind turbines are manufactured in the power range of a
few hundred kilowatts to several megawatts, so that hundreds of them must be deployed to equal
the output of a typical steam electric power plant. Maintenance of this many units at a remote or
V
)
/
21
Equation (7.15) is ca
lle
d a Rayleigh distribution. It satisfies the integral conditions that
0
p
{
V
}
dV
=
1
and
0
Vp
{
V
}
dV
=
V
.