Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
a
After extraction
P1
*
P
C
18U
FA
P2
I
P
v
P3
C
1
I
C
16U
FA
C
28
X
X
Ps
Ps
X
X
Ps
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
Retention time
b
After base hydrolysis
C
1
I
I
P1
Ps
P3
St
P2
Ps
Ps
X
C
20
C
28
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
Retention time
c
After base and acid hydrolysis
X
X
X
X
X
C
20
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
C
28
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
Retention time
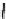
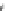
Fig. 2.2
Partial ion chromatogram showing py-GC/MS analyses of modern
Agave americana
cuticle and associated tissue (
a
) after lipid extraction (Residue 1); (
b
) after saponifi cation (Residue 2);
and (
c
) after saponifi cation and acid hydrolysis (Residue 3). Note the presence of
n
-alkane/alk- 1-ene
homologues in all three fractions. Ps: polysaccharide pyrolysis products; P: phenol; Pn: alkyl
phenols, where n denotes the number of carbon atoms in the alkyl component, P
v
: vinyl phenol
(derived from cutin), I: indole; C
1
I: methyl indole; St: styrene; C
16U
FA: C
16
unsaturated fatty acid,
and C
18U
FA: C
18
unsaturated fatty acid, X:
n-
alkane/alk-1-ene homologues (Cn refers to the carbon
chain length). *contaminant. Peak at C
29
n
-alkane is exaggerated due to co-elution with a contaminant



































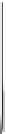












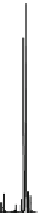



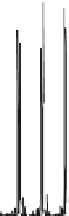






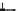





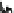
































































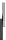
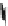











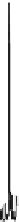



























































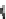

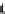





























































































































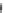









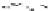




















Search WWH ::

Custom Search