Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
a
P
Miocene fossil from Clarkia
Pr
P1
C
20
XX
X
X
X
P1
X
X
X
X
X
B2
G1
G2
P2
G3
B1
G5
G4
P2
B3
C
20
Pr
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
Eocene fossil from Axel Heiberg
b
G3
G2
Pr
P1
G1
C
20
G4
X
G5
X
P
X
X
X
X
X
P1
P2
Lv
X
X
X
X
X
B2
B1
P2
Ps
C
20
Pr
B3
XX
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
Eocene fossil from Republic
B2
c
B1
P
P1
XX
X
X
X
X
X
C
20
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
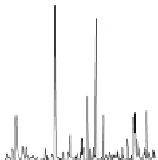
Retention time
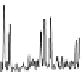
Fig. 1.6
Total ion chromatogram from Py-GC-MS analysis of fossil
Metasequoia
from (
a
)
Miocene of Clarkia, (
b
) Eocene of Axel Heiberg (Canada), (
c
) Eocene of Republic. Note the
presence of long-chain
n
-alkane/alk-1-enes (X); carbon chain length is denoted by Cn. Other sym-
bols as Fig.
1.1
. Note lack of preserved biopolymers in fossil from Republic, presence of lignin
from Clarkia and both lignin and cellulose from Axel Heiberg. All fossils have a macromolecular
aliphatic content C
27
and above (displayed inset for Clarkia and Axel Heiberg ) that is absent in the
modern leaf
Experimental Heating
Modern
Metasequoia
needles were experimentally heated in confi ned conditions at
350 °C, 700 bars, without any chemical treatment, to investigate the transformation
of biological precursors at this elevated pressure and temperature. Thermodesorption
(TD-GC-MS) at 310 °C yielded primarily
n
-alkanes from C
15
-C
29
, alkyl phenols
and alkyl napthalenes. Py-GC-MS analysis of the residue following thermodesorp-
tion yielded
n
-alkane/
n-
alk-1-ene homologues from C
8-32
, indicating the presence of
an
n
-alkyl macromolecular component (Fig.
1.7
). The most abundant homologues
were those from C
10
-C
18
. The longer chain length
n
-alkanes (>C
27
) showed an odd
over even predominance. Apart from the aliphatics, other important pyrolysis prod-
ucts included phenol and its alkyl derivatives and benzene and its alkyl derivatives.
The guaiacyl-related lignin moieties, polysaccharides and vinyl phenol evident in

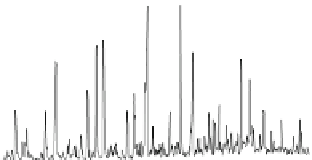





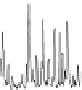






















Search WWH ::

Custom Search