Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
a
C
16
+ C
18
fatty acid
C
15
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
C
16
FA
C
18
FA
X
C
9
C
19
X
X
X
X
b
Shrimp cuticle + CaCO
3
C
15
C
2
P
m/z
83+85
X
X
X
X
C
1
In
C
16
FA
C
3
Py
X
X
X
C
9
C
3
P
X
X
X
X
C
2
Py
C
2
Id
C
1
P
C
1
Py
C
16
FA
C
3
Id
A
B
1
C
2
Pyr
A
B
2
Retention time
Fig. 8.3
Partial pyrolysis-GC/MS chromatograms of (
a
) matured mixture of C
16
and C
18
fatty
acids with kaolinite and (
b
) shrimp cuticle matured in the presence of calcium carbonate.
Annotations as in Fig.
8.2
. The analysis time was 55 min
Discussion
The results of these artifi cial maturation experiments reveal the source of the ali-
phatic component in fossil arthropod cuticles (Table
8.1
). Previous experiments
(Stankiewicz et al.
2000
) involved maturation of cuticle of the emperor scorpion,
which had been solvent-extracted (but not saponifi ed) and then degraded experi-
mentally for 8.5 months in a bacterial inoculum. The sample matured at 260 °C
generated abundant phenol during Py-GC/MS but markers directly related to chitin
and protein were absent showing that thermal maturation alone can degrade chitin.
C
5
to C
20
n
-alk-1-enes and
n
-alkanes were present, indicating the presence of an
n
-alkyl component. Thermal maturation at 350 °C resulted in more extensive




























































































































































































































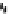





















Search WWH ::

Custom Search