Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
a
Matured cutin (pretreated tomato peel)
C
16
FA
C
11
FA
C
15
C
10
FA
C
9
FA
X
X
C
15
FA
X
X
C
12
FA
X
C
14
FA
C
13
FA
P
2
P
1
X
C
8
X
B
2
X
X
P
3
X
X
X
B
1
b
Matured tomato mesocarp
X
C
15
X
P
2
C
16
FA
X
C
1
In
P
1
X
X
C
18
FA
C
20
X
P
3
X
In
X
X
X
X
X
B
1
X
X
P
B
2
X
X
m/z
83+85
C
15
X
X
C
16
FA
X
X
C
20
X
C
8
X
C
26
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
Retention time
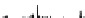
Fig. 5.4
Partial ion chromatograms showing the pyrolysis-GC/MS analysis of (
a
) modern Tomato
peel/Cutin and (
b
) tomato mesocarp,
m/z
85 + 83 mass chromatogram focuses on the distribution
of alkane/alkene homolgues. For key to symbols see Fig.
5.2
.
M/z
85 + 83 mass chromatogram
focuses on the distribution of
n
-alkane/alkene homolgues
an aliphatic component consisting of fatty acyl moieties from
n
-C
8
to
n
-C
16
(C
16
FA
the most abundant) and
n
-alkane/alk-1-ene homologues ranging from
n
-C
9
to
n
-C
18
(Fig.
5.4a
). Only trace abundances of the longer chain homologues were detected.
Thus, cutin contributes to the low-molecular-weight aliphatic pyrolysis products.






























































































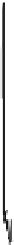




































































































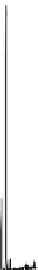



































































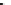










Search WWH ::

Custom Search