Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
P
G
G
C
16
FA
Ps
G
P
v
Ps
S
G
P
1
S
C
18
FA
S
C
14
FA
Ps
C
27
C
20
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
b
Castanea
leaf matured without pretreatment
C
27
P
1
∗
X
C
15
C
18
FA
X
P
2
C
1
In
C
16
FA
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
In
X
C
29
P
X
P
3
C
2
Pyr
X
X
X
X
B
1
X
B
2
X
X
O
O
c
Castanea
leaf matured after extraction and saponification
P
3
P
1
P
2
P
2
P
4
P
3
C
1
Py
P
3
P
2
B
2
B
1
Retention time
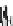
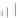
Fig. 5.2
Partial ion chromatograms showing the pyrolysis-GC/MS analysis of modern
Castanea
leaf; (
a
) without maturation, (
b
) matured at 350 °C, 700 Bars for 24 h without any chemical pre-
treatment, and (
c
) matured after extraction followed by saponifi cation. Note the presence of
n
-alkane/alkene homologues in high relative abundance in (
b
) ranging from C
9
to C
31,
including long
chain homologues suggesting the presence of a strong
n
-alkyl component similar to that encountered
in leaf fossils, and the lack of these in (
c
).
B
n
: Benzene derivative,
C
n
FA
: Fatty acyl moieties,
P
: Phenol,
P
n
: phenol derivatives (where
n
refers to the carbon chain length of the alkyl component)
C
2
Pyr
C
2
: pyrrole derivative, In: indole,
C
1
In
: methyl indole,
C
1
Py
: methyl pyridine,
Ps
: polysaccha-
ride pyrolysis products,
G
: guaiacyl units,
S
: syringyl units and
C
16
: fatty acid (C
16
FA), * contaminant.
X n
-alkane/alkene homologues and
O n
-alkanes, C
n
referring to the carbon chain length






























































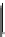


















































































































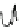





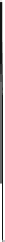






















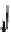
















































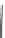








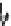
















































































































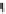



































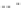
















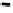













Search WWH ::

Custom Search