Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
Sediment associated with fossil conifer
a
B3
B4
B2
Pr2
?
13
∗
23
Pr1
11
21
P
2
?
16
N
18
25
27
30
b
B2
Pr2
Pr1
B3
22
B
4
2
0
2
5
28
22
m/z
74+87
16
20
14
6
8
24
18
12
10
26
28
Retention time
Fig. 4.6
(
a
) Partial Py-GC-MS total ion current chromatogram of sediment associated with fossil
conifer. (
b
) Partial TMAH/Py-GC-MS total ion current chromatogram of sediment associated with
fossil conifer showing the presence on n-alkane/n-alkene homologues, benzene derivatives and pris-
tenes. The m/z 74 + 87 mass chromatogram reveals the distribution of fatty acid methyl esters, FAME
(d); C22 followed by C19 are the most abundant (cf. Fig.
4.5
, thermochemolysis of fossil conifer,
where the acid distributions are different). Peak labels are the same as in Fig.
4.2
. *Contaminant
maximising at C
13,15
and C
23
largely consistent with the py-GC-MS results. FAME
ranging from C
6
toC
26
and dominated by C
16
were the most abundant, followed by
C
14,
C
18
and C
8
homologues (Table
4.1
). Long-chain acids from C
17
toC
26
(except for
C
18
and C
22
) are the least abundant. Except for C
16
FAME, the acids are less abun-
dant than the corresponding alkane/alkene peaks.










































































































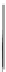





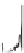
































































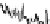















































































































































































































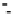










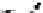


















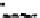




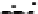






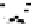







Search WWH ::

Custom Search