Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
living bodies at very low concentration, under 1 ppb. Some of these molecules can act as
endocrine disruptors and then have a very strong effect at trace amounts on the hormonal
equilibrium of the living bodies. The sources of these organic molecules are numerous and
probably scattered from very different applications. However, the greater part comes out
of the medical centers, hospitals, and medical analysis laboratories, which have a daily role
in more and more clinical treatments. As the number of these important sources is very
limited, it is recommended to remove these molecules before they low into the wastewater
collection system.
Owing to the high chemical stability of some of these compounds, and the fact that they
are very frequently mixed with solvents, speciic degradation processes should be used.
The supercritical water process allows a full degradation of organic molecules. The super-
critical state is a high-pressure/high-temperature state of a liquid or a gas. It is already
used, and for a long time, in the food industry with supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO
2
)
for decaffeinated coffee, for instance. CO
2
has a critical point at 31.3°C and 72.9 atm. Water
has a critical point at a much higher pressure and temperature, and until now, the appli-
cations of supercritical water have been limited because of these operating conditions.
However, the use of nanomaterials allows one to conduct remediation processes in super-
critical or subcritical water conditions.
3.2 Water Remediation in Supercritical Conditions
3.2.1 Supercritical State
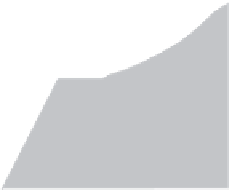
Water is commonly found under three states: solid (ice), liquid (water), and gas (water
vapor). The phase diagram of water shows these different domains (Figure 3.1). There are
equilibria between every couple of states. When the water vapor is compressed to high
pressure (A) at constant temperature, its density increases and the gas becomes more
and more dense, and liqueies above a pressure that depends on the temperature. To the
Pressure
(atm)
Supercritical state
Liquid
(water)
221
Critical point
221 atm, 375°C
Solid
(ice)
B
0.006
A
Gas
(water vapor)
Triple
point
Temperature
°C
375
0.01
FIGURE 3.1
Phase diagram of water.