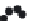Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
to be 2.55, indicating the presence of a relatively large amount of disordered graphite com-
ponents in ACF. This disorder increases during nickel impregnation. As also observed,
CNF grown on ACF retains short-range graphitic characteristics with an
I
D
/
I
G
ratio of 2.89.
36.8 ACF/CNF as Adsorbents
The adsorption capacity of an adsorbent may be tested under batch and/or low conditions.
In a typical batch experiment, a ixed amount of adsorbent is mixed with a ixed volume of
water containing an initially predetermined concentration of the solute and is allowed to
come to equilibrium at a constant temperature. The concentration of the solute in the adsor-
=
(
0
, where
C
0
and
C
are the aqueous-phase solute concentrations before and after equilibrium is attained.
V
is
the volume of the solution in contact with the adsorbent of weight
w
. Figure 36.9 presents
the equilibrium concentrations of the luoride ions in the solid phase as a function of the
aqueous-phase concentration for ive types of samples: the ACF substrate, Al-ACF (ACF
impregnated with Al), CNF, and Al-CNF with and without sonication (acid treatment).
The lines regressed through the data are essentially the equilibrium isotherms of luoride
ions vs. Al-impregnated carbon ibers at 35°C. As observed, the solid-phase concentrations
are between 0.10 and 15 mg/g, corresponding to the liquid-phase concentrations between
0.1 and 50 mg/l. For each sample, the data are best explained by the Freundlich isotherm,
q
=
K
×
C
n
, where
q
is the amount of adsorbed luoride ions in milligrams per gram of ACF,
K
is the Freundlich constant, and
n
is the power of isotherm. The values of the constant
n
less than unity indicate a favorable adsorption for the systems reported here.
VC
C
bent phase is theoretically determined by the mass balance,
q
w
100
Al-CNF (with sonication)
Al-CNF (without sonication)
Al-ACF
CNF
ACF
Freundlich equation
q = K
×
C
n
10
1
0.1
0.0
0.01
0.1
Aqueous-phase fluoride concentration (mg/l)
1
10
100
FIGURE 36.9
Comparative performance of Al-CNF (with and without sonication), Al-ACF, CNF, and ACF for luoride
removal. Solid lines show Freundlich isotherms,
q
=
K
×
C
n
; where
K
= 1.30, 0.85, 0.59, 0.17, 0.06 and
n
= 0.61, 0.69,
0.75, 0.59, 0.41 for Al-CNF (with and without sonication), Al-ACF, CNF, and ACF, respectively. (From A. Gupta
et al.,
I&EC Res
., 48, 9697, 2009.)