Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
0 nM
10
30
50
100
150
200
250
335
420
500
1000
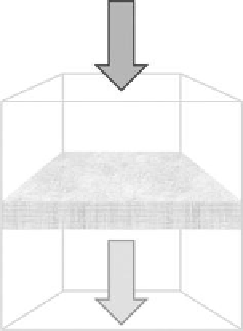
Live bacteria in
Blotter paper containing
silver nanoparticles
DGG 2011
Dead bacteria out
500
600
700
800
900
Wavelength (nm)
FIGURE 26.7
(a) Schematic representation of passing water containing bacteria through Ag NPs-incubated blotter paper.
(Adapted from Dankovich, T.A., and Gray, D.G.,
Environ. Sci. Technol
., 45, 1992, 2011. Copyright with permission
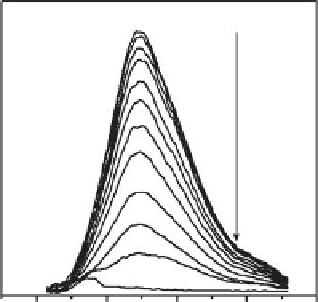
from American Chemical Society.) (b) PL spectra (λ
ex
= 489 nm) of GSH-AgNCs (100 nM) in the presence of Cys
solutions of different concentrations. (Adapted from Yuan, X. et al.,
Anal. Chem.
, 85, 1913, 2013. Copyright with
permission from American Chemical Society.)
Clusters are predicted to exhibit superior antimicrobial activity due to smaller size and
high surface-to-volume ratio.
Yuan et al
.
52
synthesized silver clusters using a cyclic reduction-decomposition method
and used them for antibacterial studies with a model microbe,
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
. The
microbe is known to cause urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and respiratory system
infections in many burn cases and immunosuppressed AIDS patients. This particular bacte-
rium is resistant to many conventional antibiotics, such as ampicillin, penicillin, and cepha-
losporin. In the experiment, red-emitting GSH-protected Ag clusters (r-Ag NCs) were used
to kill the bacteria. This study showed that a very little amount of cluster (8 μg) was enough
to inactivate the microbe. Growth of bacteria culture was completely stopped after treating
with 500 μM of cluster (on the basis of Ag atoms). Eficiency of the r-Ag NCs for antibacte-
rial activity was comparable to that of chloramphenicol, a common antimicrobial agent. For
understanding the cause of inactivation of bacterial growth, the level of the intracellular
reactive oxygen species (ROS) was measured. There was a 6-fold increase in the oxidized
2',7'-dichloroluorescein (DCF) concentration in the r-Ag NCs-treated bacteria culture. This
conirmed that the formation of ROS was due to the presence of silver clusters. The eficiency
of silver in the form of clusters was higher compared with the NPs (>2 nm size) form. They
also proposed that the reduction in side effects originated due to silver can be minimized
(when clusters are used), as in other studies where larger-sized NPs were used.
Cysteine (Cys) is one of the essential thiol (-SH)-containing amino acids. It is recognized
to be a potential neurotoxin. Deicient levels of Cys cause many health problems such as
hair depigmentation, liver damage, slowed growth, skin lesions, weakness, and edema.
It is important to have sensors for the selective and sensitive detection of Cys using a
simple colorimetric/luorometric method. Yuan et al.
53
have used GSH-protected Ag NCs
for selective detection of Cys at <3 nM levels. Fluorescence of Ag clusters was quenched
due to the interaction of Ag from clusters with the S in Cys, leading to the decomposi-
tion of clusters into thiolate-Ag(I) complexes (Figure 26.7b). Decomposition of clusters was
also observed in the color change from brown to colorless along with the disappearance