Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
metals are ruthenium (Ru), rhenium (Re), rhodium (Rh), copper (Cu), silver (Ag), gold (Au),
palladium (Pd), platinum (Pt), osmium (Os), mercury (Hg), and iridium (Ir). In the bulk
state, noble metals exhibit insolubility in water, metallic luster, malleability, electrical con-
ductivity, and no catalytic activity. These properties change when the size of the metal is
reduced. They (especially Cu, Ag, and Au) start showing dispersion in water when the size
is reduced to nanoscale range. The wine red solution of Au obtained in Faraday's experi-
ment contains inely divided metal species that absorb visible light. Gold nanoparticles
(Au NPs) start exhibiting catalytic activity in many reactions such as oxidation, coupling,
and reduction.
4
Noble metal nanosystems (NMNs) can be broadly divided into four types: three-, two-,
one-, and zero-dimensional (D) structures. Shapes such as stars/lowers (3D), ilms/plates/
networks/layers (2D), ibers/tubes/rods/wires (1D), and NPs/quantum dots (QDs)/quan-
tum clusters (QCs) (0D) are corresponding examples. QDs and QCs are structures whose
sizes are typically 2-4 nm and <2 nm, respectively.
5
Optical properties, such as absorp-
tion, emission, and optical activity; physical properties; and chemical properties vary with
size and shape. Silver and gold NPs protected with citrate show light yellow and wine
red colors, with absorption bands at 400 and 520 nm, respectively for 10-15 nm particles.
These absorption bands are due to collective oscillations of conduction band electrons
when electromagnetic radiation interacts with them and are due to surface plasmon reso-
nance (SPR). Gold nanorods, in contrast, exhibit two SPRs corresponding to longitudinal
and transverse modes of plasmons. Different morphologies such as triangles, wires, and
polygons exhibit multiple SPRs.
The size of QCs is in between NPs and molecules. Clusters of precise numbers of metal
atoms and protecting ligands possess molecular absorption and luminescence properties
(Figure 26.1). Au
25
(SC
2
H
4
Ph)
18
, Au
38
(SC
2
H
4
Ph)
24
, and Ag
32
(SG)
18
are some of the examples
of monolayer-protected noble metal clusters.
6
Au
25
(SC
2
H
4
Ph)
18
is a thoroughly investi-
gated QC along with x-ray crystal structure and its size is 1.2 nm with a HOMO-LUMO
gap of 689 nm (1.8 eV). It exhibits absorption bands at 451 nm (2.75 eV) and 400 nm (3.1 eV)
(a)
(b)
S
Au
Au
Emission
Excitation
450
600
750
900
400
600
800
Wavelength (nm)
Wavelength (nm)
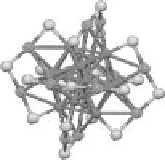
FIGURE 26.1
(See color insert.)
(a) UV/Vis optical absorption spectrum of Au
25
(SG)
18
cluster. (b) Photoluminescence spectra of
Au
25
(SG)
18
, which exhibits emission at 690 nm. (Adapted from Shibu, E.S. et al.,
J. Phys. Chem C
., 112, 12168, 2008.
Copyright with permission from American Chemical Society.) Inset: crystal structure of Au
25
(SCH
2
CH
2
Ph)
18
.
Total structure is assumed as a shell of six (-RS-Au-SR-Au-SR-) units sitting on an Au
13
core. (Adapted from
Zhu, M. et al.,
J. Am. Chem. Soc
., 130, 5883, 2008. Only Au and S atoms are shown. Copyright with permission
from American Chemical Society.)