Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
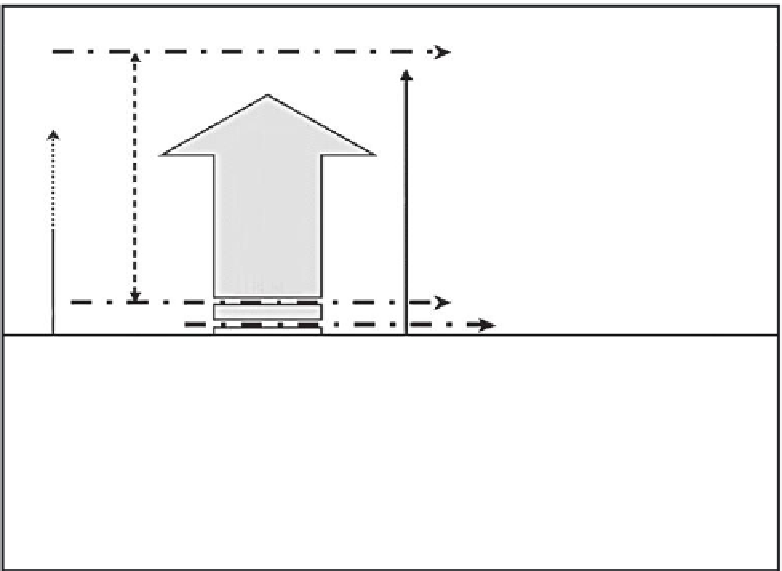
Desirable sustainability level
Essential sustainability level
Necessities
Needs
Basic sustainability level
Requirement class
Community requirements
Key sustainability indicators
Physical health status, life/health
expectancy
Needs
Food, water, shelter, clothing
Necessities
(
minimum
standard
of living)
Primary education, basic
health services, social security
Literacy level, unemployment
levels, mortality and fertility rates,
crime rates, social stability
Desires (luxuries)
(
varying
standards
of living)
Entertainment, public comforts,
personal luxuries
GNP, GDP, number of cars per
family, average income
FIGURE 15.1
Sustainability levels. (From Mani, M. et al.,
Sustainability and Human Settlements
. Sage Publications, New Delhi,
Thousand Oaks, London, 2005.)
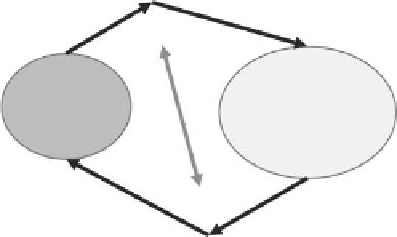
Animals
O
2
CO
2
Plants
FIGURE 15.2
Simple closed cycle (illustrating that everything in the natural world is cyclic).
community's luxurious wants and desires. These can include artifacts, exotic decorations,
lavish clothing including fur, etc.
Modern society should seek to achieve a healthy living environment that enables fulill-
ment of societal, economic, and social (including political) needs, by trying to achieve a
balance between resource needs for human development and protection of environmental
vitality. Sustainable development thus has a bipolar objective, the irst focusing on equi-
table human development and the second addressing the issue of maintaining, protecting,