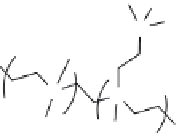Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(Figure 12.7).
45
The functionalized
silica gel was made into a cartridge
ilter, and the biocidal eficacy against
the bacterial pathogens
S. aureus
and
E. coli
O157:H7 showed complete 6 log
inactivation of the two bacterial spe-
cies within 30 s of contact.
45
Moreover,
the biocidal
N
-halamine moieties of
the coated silica gel particles could
be regenerated by simple exposure
to dilute bleach. Potential uses of
the biocidal silica gel includes water
disinfection.
(a)
OH
(b)
*
Si
O
*
n
O
Cl
N
N
O
O
N
N
O
H
FIGURE 12.7
(a) Structure of
N
-Chlorohydantoinyl siloxanes employed to
create antimicrobial composite. (b) Silica gel particle with
covalently attached
N
-Chlorohydantoinyl siloxanes. (Adapted
from Liang, J. et al.,
J Appl. Polym. Sci.
101, 3448, 2006.)
12.2.2.2 Polymer-Silica Composites
Although silver has attractive antibacterial activities, its primary shortcoming is that the
particles are easily washed out since they are just impregnated into the material. This might
reduce the disinfection eficiency over time and release of high amounts of silver into the
water might be toxic to humans. Hayden and coworkers developed a new sand iltration
water disinfection technology that relies on the antimicrobial properties of hydrophobic
polycations (
N
-hexylated PEI) covalently attached to the sand's surface (Figure 12.8).
46
The
applicability of the ilter in water disinfection was evaluated both with water spiked with
E. coli
and with efluents from a wastewater treatment plant. In the case of water spiked
with
E. coli
, >7-log reduction in bacterial count was achieved, whereas with wastewater
efluent samples, the
E. coli
concentration was reduced to <2 logs. This low inactivation
capability of the polymer-sand ilter in case of the wastewater efluent samples compared
with the aqueous sample might be due to the presence of particulate matter that diminishes
the contact between the immobilized polycation and the suspended bacteria. Preliminary
sand-washing methods using PBS and ethanol tested to assess potential “regeneration”
approaches showed that these procedures refresh the bactericidal activity of the polymer.
46
These polymer-sand composites and
N
-halamine hybrid composites have a lot of advan-
tages over conventional disinfectants in terms of no harmful disinfection by-products and
reduction of energy consumption. They have potential applications in water disinfection,
particularly in developing countries.
12.2.3 Inorganic-Organic TiO
2
Composites
Photocatalysis applications of wide-reaching impor-
tance include degradation of environmental pollutants
in aqueous contamination and wastewater treatment.
One of the most popular applications of photocatalytic
materials is the photodegradation of bacteria that can be
used in water disinfection. The ideal antimicrobial pho-
tocatalytic materials should possess advantages such as
high and lasting antibacterial eficacy, environmental
safety, low toxicity, and simplicity in fabrication. TiO
2
has been the most widely researched photocatalyst, but
suffers from low eficiency and a narrow light response
Sand
particle
FIGURE 12.8
Covalently modiied sand particle with
hydrophobic polycation,
N
-hexylated
poly ethylenimine.