Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
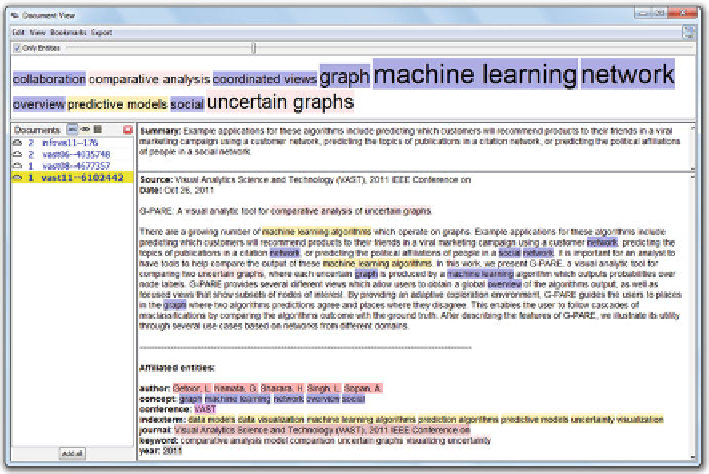
Fig. 9.5
The document view in Jigsaw
Jigsaw is designed to extract entities and relationships from unstructured text
and provide users with a broad range of interactive views to explore the identified
entities and how they are related. For example, given a set of scientific publication,
Jigsaw will identify entities such as authors, concepts, and keywords.
Jigsaw provides several forms of representations of the underlying data.
Figure
9.5
shows the interface of its document view. The top of the view shows
a tag cloud display in which the size of a term reflects the frequency of the term.
We can easily learn that the data is mainly about machine learning and network.
The lower part of the view is split into two parts. The part on the left shows a
list of the documents the user has browsed. The entry of the current document is
highlighted in yellow. Its content is display in the window on the right. Inside the
content window, a brief summary is displayed on the top, followed by the text of the
document. Entities identified in the text are highlighted. For example, comparative
analysis and uncertain graphs are highlighted in the title of the 2011 VAST paper.
The authors of the paper are identified along with other entities such as concepts
and the source of the document.
Figure
9.6
shows the List View of Jigsaw. The List View can display multiple lists
of entities simultaneously and highlight how selected entities in one list are related
to entities in other lists. The example in Fig.
9.6
displays three lists of entities, a list
of concepts, a list of authors, and a list of index terms. The source documents are
the papers of the InfoVis and VAST conference proceedings. The authors selected
in the middle are coauthors of my publications in InfoVis and VAST. The highlight
Search WWH ::

Custom Search