Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
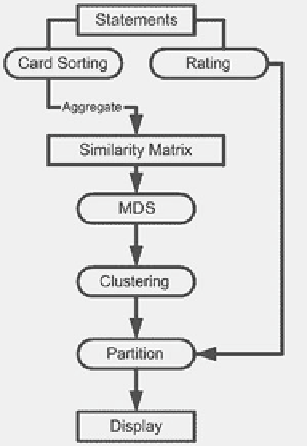
Fig. 3.39
The procedure
used for concept mapping
When participants sorted statements into piles, they also rated each statement
on one or more variables. Most typically, each statement was rated for its relative
importance on a 5-point scale, from 1 for unimportant through 5 for extremely
important. The results of such rating were subsequently used as a thematic overlay
on top of the base map (See Fig.
3.40
).
3.4.2
Clustering
There are two broad types of approaches to hierarchical cluster analysis:
agglom-
erative
and
divisive
. In agglomerative, the procedure starts with each point as its
own branch end-point and decides which two points to merge first. In each step, the
algorithm determines which two points and/or clusters to combine next. Thus, the
procedure agglomerates the points together until they are all in one cluster. Divisive
hierarchical cluster analysis works in the opposite manner, beginning with all points
together and subsequently dividing them into groups until each point is its own
groups. Ward's method is an agglomerative approach.
Three methods of analysis are closely related to MDS. These are principal
component analysis (PCA), correspondence analysis (CA) and cluster analysis.
Principal components analysis (PCA) is performed on a matrix A of N entities
observed p variables. The aim is to search for new variables, called principal
components, which are based on a linear combination of the original variables
and they can account for most of the variation in the original variables. When
these distances are Euclidean distances, the coordinates contained in X do represent
Search WWH ::

Custom Search