Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
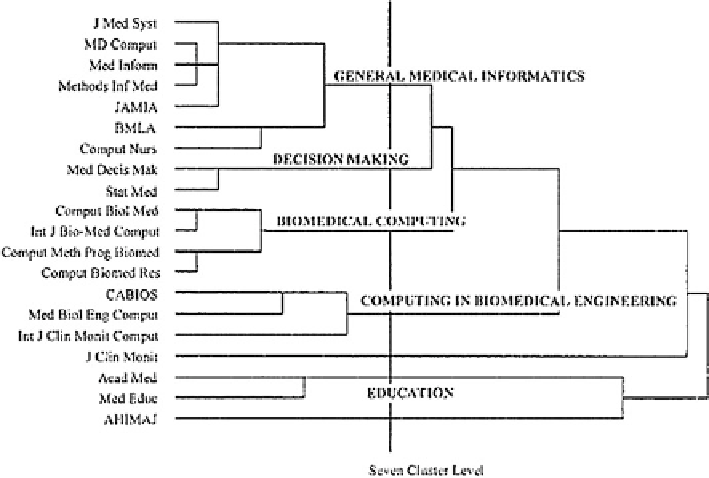
Fig. 3.30
Cluster solution for SCI co-citation data (Reproduced from Morris and McCain (
1998
).
Note that “Comput Biol Med” and “Int J Clin Monit Comput” belong to different clusters)
increases exponentially as the stress value decreases. After all, if the original data
is of high-dimension in nature, it is not always possible to find a perfect fit in a
lower-dimensional space. For example, it is almost certain that we have to settle on
a higher stress value when mapping N statements on a general topic than mapping
the distances of N cities. Furthermore, if the distances among cities were measured
by something of higher dimension in nature, such as the perceived quality of life,
it would be equally unlikely for MDS to maintain the same level of goodness of
fit. Indeed, Trochim (
1993
) reported that the average stress value across 33 concept
map projects was 0.285 with a range from 0.155 to 0.352. After all, the goal of MDS
mapping is not merely to minimize the stress value; rather, we want to produce a
meaningful and informative map that can reveal hidden structures in the original
data.
3.3.3
INDSCAL Analysis
INSCAL was developed by John Carroll and J. Chang of Bell Telephone Laborato-
ries in the 1970s to explain the relationship between subjects' differential cognition
of a set of stimuli, or objects. For N subjects and p objects, INDSCAL takes a set
of N matrices as its input. Each matrix is a symmetric p
p matrix of similarity
Search WWH ::

Custom Search