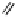Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
oligomers are formed mostly through intermolecular C-O oxidative
coupling between ellagitannin monomers was recently obtained with the
enzymatic formation of cornusiin E from tellimagrandin II (
1
) (Niemetz
and Gross, 2003). Oligomers of diverse structures are classified
according to the coupling mode between the monomers involved, as
described in Chapter 1.
2.2.1 Oligomers linked with a dehydrodigalloyl group
GOG-type oligomers with a dehydrodigalloyl (DHDG) unit have been
found in the
Rosaceae
,
Coriariaceae
,
Nymphaeaceae
, and
Tamaricaceae
. Of these, the dimers from rosaceous and coriariaceous
plants, for example, agrimoniin, gemin A, and coriariin A (see Chapter
1), have an
m
-GOG unit produced by intermolecular C-O coupling
between the O-1-linked galloyl group of each monomer, while the
dimers found in the
Nymphaeaceae
and
Tamaricaceae
have the
m
-GOG
unit connected between the O-1 position of one monomer and the O-2
position of the other monomer, as exemplified in nupharin E (
61
)
(Ishimatsu
et al.
, 1989b) and hirtellin A (
62
) (Yoshida
et al.
, 1991c).
OH HO
OH
HO
OH
HO
O
O
OH
OH
HO
OH
HO
O
O
HO
HO
O
O
O
OH
OH
HO
HO
HO
O
O
O
2
O
O
O
O
O
HO
O
O
O
OH HO
OH
HO
2
OH
HO
O
O
OH
O
HO
OH
OH
O
OH
m
-GOG
HO
O
OH
O
O
OH
OH
O
O
HO
OH
OH
HO
OH
O
O
O
1
HO
m
-GOG
O
OH
HO
O
OH
O
HO
HO
O
O
O
OH
HO
O
HO
O
O
1
O
O
O
O
O
HO
O
HO
Nupharin E (
61
)
O
OH
OH
OH
OH
Hirtellin A (
62
)
HO
OH
HO
OH