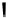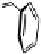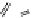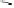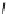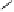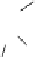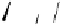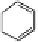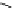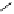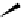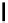Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
as
12
-
17
. Here, one can ask again the question of whether the generation
of each of these compounds is under enzymatic control. Probably not, for
the departure of the OH group from the C-1 position of the monomers
1
/
2
or
3
/
4
, which could be chemically promoted under acid catalysis,
would result in the formation of a stable benzylic cation intermediate
27
or
28
that could then be quenched by various nucleophilic species such
as the ones mentioned above and conceivably others (Fig. 9.7).
HO
HO
HO
HO
OH
OH
HO
HO
O
O
O
O
HO
HO
β
-orientation
O
O
O
O
HO
HO
Nu
+H
+
/-H
2
O
Nu
O
O
1
and/or
2
1
O
O
O
O
OH
O
O
OH
HO
HO
O
O
O
O
HO
HO
OH
OH
HO
HO
OH
OH
OH
OH
HO
HO
HO
HO
27
HO
HO
HO
HO
OH
OH
HO
HO
O
O
O
O
HO
HO
O
O
O
O
HO
HO
Nu
+H
+
/-H
2
O
O
Nu
O
1
3
and/or
4
GO
GO
O
O
OH
O
O
OH
O
O
OH
OH
OH
OH
OH
OH
HO
HO
HO
HO
28
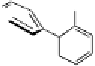
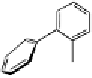
Fig. 9.7 Acid-catalyzed condensation reactions of
C
-glycosidic ellagitannins.
This chemistry taking place at the C-1 position of
C
-glycosidic
ellagitannins featuring a free benzylic alcohol function at that position,
i.e.
, not only monomers such as
1
/
2
or
3
/
4
but also oligomers like the
roburins A/D (
5
/
6
), is characterized by another intriguing apparent
specificity. Nucleophilic substitution reactions proceed in a strict