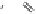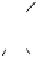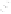Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
HO
HO
OH
OH
HO
O
O
HO
HO
O
OH
O
O
HO
H
OR
O
HO
OH
RO
HO
HO
OH
O
O
OH
OH
O
HO
OH
O
O
HO
OH
OH
O
OH
O
HO
O
HO
H
HO
OH
O
Camelliatannin B : R = H
Malabathrin A : R = G
RO
O
O
O
O
H
HO
Camelliatannin F : R = H
Malabathrin E : R = G
HO
OH
HO
O
1.3.3.2
Biomimetic synthesis of C-glycosidic ellagitannins
Casuarinin was biomimetically synthesized through an acid-catalyzed
intramolecular phenol-aldehyde coupling reaction of liquidambin (Fig.
1.3, see also Fig. 9.6 in Chapter 9), an aldehydic ellagitannin presumed
to be the key biosynthetic precursor of
C
-glycosidic ellagitannins (Okuda
et al
., 1987). The complex tannins camelliatannins A and B were
hemisynthesized by condensation of casuariin with (-)-epicatechin (Fig.
1.3), and also by conversion of camelliatannins E and C, respectively, via
a treatment with polyphosphoric acid (Fig. 1.4). The transformation of
camelliatannin A into cammelliatannin F, featuring a cyclopentenone
ring, was achieved by heating camelliatannin A in a mixture of ethanol
and acetic acid (Fig. 1.4, Hatano
et al
., 1995).
1.3.4 Oligomerization of ellagitannins leading to pentamers
The first oligomeric hydrolyzable tannin isolated in 1982 was agrimoniin
(
vide supra
), which remarkably displays α-glycosidic linkages on both of
its constituting monomeric units (Okuda
et al
., 1982b). Its isolation was
followed by that of gemin A (
vide infra
), a dimer having both α
and β
linkages (Yoshida
et al.
, 1982), and gemins B-F (Yoshida
et al.
,