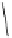Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
much higher concentrations of ellagitannins, free ellagic acid and its
glycosides than the flesh (Aaby
et al.
, 2005).
OH
HO
O
OH
HO
HO
HO
O
O
O
OH
O
O
O
HO
HO
O
O
O
O
OH
HO
OH
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
OH
O
OH
HO
O
OH
O
O
HO
OH
OH
HO
HO
OH
OH
HO
OH
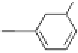
Fig. 8.3 Sanguiin H-6, an ellagitannin in raspberries, cloudberries and strawberries.
HO
HO
OH
OH
Koponen
et al
. (2007) analyzed the content of ellagitannins (as
ellagic acid equivalents after acid hydrolysis) in selected foods consumed
in Finland, including berries, fruits, vegetables and processed products.
Ellagic acid was found in 9 of 33 selected food items, and the total
ellagic acid content varied from 10 to 3300 mg/kg (Table 8.1). Ellagic
acid was mostly present as ellagitannins, and the relative amount of free
ellagic acid and its glycosides (
i.e.
, non-tannin ellagic acid) was less than
6%, and in most cases only 1-2%. Berries of the family
Rosaceae
(cloudberries, raspberries, strawberries and rose hips) contained high
levels of ellagic acid equivalents, whereas minor levels were found in sea
buckthorn (family
Elaeagnaceae
). The total ellagic acid concentrations
in commercial raspberry and strawberry jams were 23-36% of those
found in the unprocessed berries. Ellagic acid compounds were detected
only in these five berries and processed products, and not in fruits,
vegetables and peanuts. These data, together with data on several other
groups of polyphenols, will be entered into the Finnish Food
Composition Database Fineli
(http://www.fineli.fi), maintained by the
National Public Health Institute of Finland. To our knowledge, there are
no other food composition databases containing ellagitannin data.