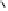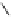Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
1.1.5 Accumulation of an ellagitannin of specific structure in a plant
Often a monomeric or an oligomeric ellagitannin is the main component
of a plant species, and the pharmacological activity of that plant is
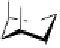
sometimes attributable essentially to that component. Geraniin is the
main component of
Geranium thunbergii
(
Geraniaceae
), making up over
10% by weight of the dry leaf. It is also the main component in other
Geranium
species (Okuda
et al
., 1980b), usually accompanied by small
amounts of analogs such as dehydrogeraniin, furosinin (Okuda
et al
.,
1982d), ascorgeraniin (Okuda
et al
., 1986a) and geraniinic acids B and C
(Ito
et al
., 1999a).
O
OH
HO
OH
OH
O
HO
HO
OH
HO
OH
O
HO
H
OH
O
O
O
O
O
OG
O
O
O
R
O
O
O
O
H
O
O
O
HO
O
O
O
OH
H
OH
HO
OH
O
OH
O
O
HO
OH
R
1
R
2
Dehydrogeraniin : R = (
β
)-OG
Furosinin : R = OH
OH
Geraniinic acid B : R
1
= COOH, R
2
= H
Geraniinic acid C : R
1
= H, R
2
= COOH
G =
OH
O
OH
Dimeric agrimoniin, oenothein B (and its trimeric variant, oenothein
A, see also Section 1.3.5) and coriariin A are also the main components
in
Agrimonia pilosa
(Okuda
et al.
, 1982b),
Oenothera erythrosepala
(Hatano
et al
., 1990a),
and
Coriaria japonica
(Hatano
et al
., 1986),
respectively, and are usually accompanied by smaller amounts of the
monomers composing these dimers and higher oligomers.