Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
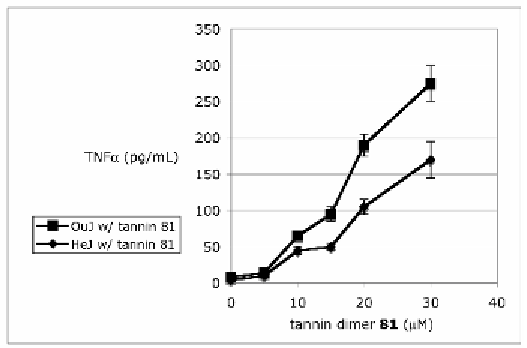
part, the same key receptor components CD14 and TLR4 that the native
ligand LPS uses. Therefore, the active tannin species appear to operate,
at least in part, as LPS (lipid A) mechanistic agonists.
Fig. 6.20 The TNFα secretion response upon treating normal OuJ mice and TLR4-
inactive HeJ mice with the dimeric tannin construct
81
.
6.5 Ellagitannins as TNF
α
Secretion Inhibitors
As discussed earlier, the systemic overproduction of TNFα in response
to LPS has been implicated in the symptoms of septic shock. In addition,
an assortment of diseases also have been linked to the chronic over-
secretion of low levels of TNFα. Since tannins appear to utilize the LPS
receptor system, at least in part, to promote TNFα release from
monocytes, the possibility of designing tannin constructs that
antagonize
rather than
agonize
LPS activity, was explored. These tannin species
would have to meet two stringent criteria for success: (1) bind
competitively with LPS (lipid A) at one (or more) of the obligate
receptors (CD14, TLR4, others?), and (2) fail to generate a signal to
synthesize/secrete TNFα. The role that galloyl groups play in receptor
recognition has not been delineated, but the preliminary data clearly
speak to their importance. In addition, the dimeric tannin species were
invariably better than their smaller monomeric analogues at eliciting