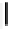Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
increasing the opportunity for replication errors. Furthermore, TNFα
recruits inflammatory factors and cells, a process that promotes
angiogenesis and provides greater access to other inflammatory factors
and cells. This action inadvertently
results in feeding and sustaining the
tumor and possibly induces eventual malignancy. Several molecular
mechanisms by which TNFα may promote cancer growth have been
proposed, including increasing cell cycle promoter levels while
decreasing levels of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, increasing ras or
c-myc (molecular switches of the growth factor receptor signaling
pathways), promoting chemo-resistance and androgen insensitivity,
activation of NF-κB (suppressing normal cell apoptosis), and inducing
DNA damage while also inhibiting DNA repair through up-regulation of
nitric oxide production (Szlosarek
et al.
, 2006).
Cl
OH
O
O
OH
N
OH
Cl
NH
2
HO
CH
3
O
O
H
O
N
O
melphalan (
4
)
O
O
H
3
C
O
NH
2
HN
OH
F
doxorubicin (
5
)
fluorouracil (
6
)
Fig. 6.3 Anticancer agents used in combination with TNFα-based drugs.
6.1.3.3
Monocyte response pathway
Bacterial components such as LPS are usually first recognized by
monocytes and macrophages through the lipid A receptor system, as will
be described in the next section. The lipid A region of LPS is recognized
by either a bound receptor cluster found on mononuclear phagocytes
(monocytes and macrophages) or by a soluble binding molecule which
activates cells that lack the lipid A receptor system. This receptor
binding leads to the transcription of more than 120 genes, including
those that code for several cytokines (Wang
et al.
, 2000). Among the
first expressed cytokines are TNFα, interleukin-1α, interleukin-1β, and
interleukin-6. These pleiotropic cytokines are first produced locally but