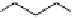Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
exotoxins are secreted peptides that may act as potent T cell activators
and lead to uncontrolled release of proinflammatory cytokines.
repeating unit
O
OH
O
HO
HO
O
O
P
O
HO
O
OAlanine
O
HO
HO
O
O
O
OH
O
OH
LTA (
3
)
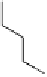
Fig. 6.2 Structure of LTA from
Staphylococcus aureus
.
6.1.3 TNF
α
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), also known as cachectin, is a
pleiotropic cytokine with broad biological capabilities. Like other
cytokines, TNFα has several advantageous properties including
accelerating wound healing, cell growth modulation, cellular
differentiation, and endogenous antimicrobial activity through activation
of the immune system. TNFα was initially identified as an anticancer
agent in 1975 when it was observed to destroy solid murine tumors
in
vivo
and was cytotoxic against several tumor cell lines (Carswell
et al.
,
1975, Helson
et al.
, 1975). Since these seminal reports detailing TNFα's
astonishing antitumor properties, its other (and major) role as a pro-
inflammatory mediator implicated in the host of diseases discussed
above has come to light. Many stimuli can activate the synthesis of
TNFα including TNFα itself, other cytokines (such as IL-1, INF-γ, IL-2,
platelet activating factor, and granulocyte macrophage-CSF), phorbol
ester, IgE, reactive oxygen metabolites, X-rays, mycobacterial proteins,
cyanobacteria, zymosan (an insoluble carbohydrate from the cell wall of